Hexachloroacetone
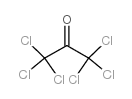
Hexachloroacetone structure
|
Common Name | Hexachloroacetone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 116-16-5 | Molecular Weight | 264.75000 | |
| Density | 1.743 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 66-70 °C6 mm Hg(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C3Cl6O | Melting Point | -3 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | >230 °F | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors are essential for breast cancer cells to control their lipid/fatty acid metabolism.
Oncotarget 6 , 19706-20, (2015) Cancer cells exhibit characteristic changes in their metabolism with efforts being made to address them therapeutically. However, targeting metabolic enzymes as such is a major challenge due to their essentiality for normal proliferating cells. The most succe... |
|
|
Coumarins as new matrices for matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometric analysis of hydrophobic compounds.
Anal. Chim. Acta 882 , 49-57, (2015) Hydrophobic compounds with hydroxyl, aldehyde or ketone groups are generally difficult to detect using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS), because these compounds have low proton affinity and are poorly ionized by MALDI. ... |
|
|
Integrated metabolomic and proteomic analysis reveals systemic responses of Rubrivivax benzoatilyticus JA2 to aniline stress.
J. Proteome Res. 14(2) , 711-27, (2015) Aromatic amines are widely distributed in the environment and are major environmental pollutants. Although degradation of aromatic amines is well studied in bacteria, physiological adaptations and stress response to these toxic compounds is not yet fully unde... |
|
|
Fluorescence emissions of imide compounds and end-capped polyimides enhanced by intramolecular double hydrogen bonds.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 , 30659-69, (2015) The structure and optical properties of a newly synthesized imide compound (DHNHPI) that forms intramolecular double hydrogen bonds (intra-HBs) were investigated. This compound exhibits intense absorption at 372 nm (ε = 5091 cm(-1) M(-1)) and strong emission ... |
|
|
Phenotypic assays to identify agents that induce reactive gliosis: a counter-screen to prioritize compounds for preclinical animal studies.
Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 13 , 377-88, (2015) Astrocyte phenotypes change in a process called reactive gliosis after traumatic central nervous system (CNS) injury. Astrogliosis is characterized by expansion of the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) cytoskeleton, adoption of stellate morphologies, and... |
|
|
Effect of organic acids on calcium phosphate nucleation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on peptide functionalized nanofibers.
Langmuir 31 , 5130-40, (2015) Carboxylate-rich organic acids play an important role in controlling the growth of apatite crystals and the extent of mineralization in the natural bone. The objective of this work was to investigate the effect of organic acids on calcium phosphate (CaP) nucl... |
|
|
Oncogenic RAS-induced senescence in human primary thyrocytes: molecular effectors and inflammatory secretome involved.
Oncotarget 5(18) , 8270-83, (2014) Oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) is a robust and sustained antiproliferative response to oncogenic stress and constitutes an efficient barrier to tumour progression. We have recently proposed that OIS may be involved in the pathogenesis of thyroid carcinoma ... |
|
|
Profile of bile acids in fetal gallbladder and meconium using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Clin. Chim. Acta 446 , 76-81, (2015) The primary bile acids found in meconium vary with the gestational age of the fetus and the intestinal location of the meconium. We determined the composition of bile acids in samples that were collected from the gallbladder and intestine.The bile-acid profil... |
|
|
Adhesive barrier/directional controlled release for cartilage repair by endogenous progenitor cell recruitment.
Biomaterials 39 , 173-81, (2015) A new design concept in controlled release chemistry is reported in this study. Unlike current depots that release drugs in all direction by an isotropic way, we demonstrate that directional release only to a clinically beneficial direction results in improve... |
|
|
Development of an in vivo glucosylation platform by coupling production to growth: Production of phenolic glucosides by a glycosyltransferase of Vitis vinifera.
Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112 , 1594-603, (2015) Glycosylation of small molecules can significantly alter their properties such as solubility, stability, and/or bioactivity, making glycosides attractive and highly demanded compounds. Consequently, many biotechnological glycosylation approaches have been dev... |