beryllium sulfate tetrahydrate
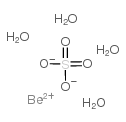
beryllium sulfate tetrahydrate structure
|
Common Name | beryllium sulfate tetrahydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7787-56-6 | Molecular Weight | 177.13600 | |
| Density | 1.713 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 330ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | BeH8O8S | Melting Point | 270ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
[Diagnosis of chronic berylliosis].
Pneumologie 53(4) , 193-8, (1999) The diagnostic value of the lymphocyte transformation test (BeLT) and the intracutaneous skin test with berylliumsulfate was addressed in 13 patients with chronic berylliosis, and 15 individuals with occupational exposure. Additionally, patients with sarcoido... |
|
|
Beryllium-stimulated release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and their soluble receptors in chronic beryllium disease.
Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 156(6) , 1884-91, (1997) Chronic beryllium disease (CBD) provides a model system in which to evaluate the antigen-stimulated, cell-mediated, immune response that leads to granulomatous lung disease. We hypothesized that beryllium salts would stimulate bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cel... |
|
|
Target organ localization of memory CD4(+) T cells in patients with chronic beryllium disease.
J. Clin. Invest. 110(10) , 1473-82, (2002) Chronic beryllium disease (CBD) is caused by exposure to beryllium in the workplace, and it remains an important public health concern. Evidence suggests that CD4(+) T cells play a critical role in the development of this disease. Using intracellular cytokine... |
|
|
Beryllium presentation to CD4+ T cells underlies disease-susceptibility HLA-DP alleles in chronic beryllium disease.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97(23) , 12717-22, (2000) Chronic beryllium disease results from beryllium exposure in the workplace and is characterized by CD4(+) T cell-mediated inflammation in the lung. Susceptibility to this disease is associated with particular HLA-DP alleles. We isolated beryllium-specific T c... |
|
|
Divergent effect of cobalt and beryllium salts on the fate of peripheral blood monocytes and T lymphocytes.
Toxicol. Sci. 119(2) , 257-69, (2011) Occupational exposure to metals such as cobalt and beryllium represents a risk factor for respiratory health and can cause immune-mediated diseases. However, the way they act may be different. We show here that the two metals have a divergent effect on periph... |
|
|
Use of proliferation tests to evaluate the effects of complexing agents on beryllium toxicity.
J. Appl. Toxicol. 29(1) , 27-35, (2009) Occupational exposure to beryllium may cause chronic beryllium disease (CBD), a granulomatous interstitial pneumonitis caused by a cell-mediated immune response with delayed hypersensitivity initiated by an electrostatic interaction with the MHC class II huma... |
|
|
Patch testing with beryllium alloy samples in guinea pigs.
Contact Dermatitis 34(3) , 196-200, (1996) An experimental study was conducted in guinea pigs for the predictive assessment of the beryllium alloy hazard in occupational exposure of the skin to beryllium compounds. Guinea pigs were sensitized to beryllium sulfate according to the maximized Magnusson a... |
|
|
Beryllium skin patch testing to analyze T cell stimulation and granulomatous inflammation in the lung.
J. Immunol. 168(7) , 3627-34, (2002) Chronic beryllium disease (CBD) is characterized by granulomatous inflammation and the accumulation of CD4(+) T cells in the lung. Patch testing of CBD patients with beryllium sulfate results in granulomatous inflammation in the skin. We investigated whether ... |
|
|
Beryllium-stimulated reactive oxygen species and macrophage apoptosis.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 38(7) , 928-37, (2005) Beryllium (Be), the etiologic agent of chronic beryllium disease, is a toxic metal that induces apoptosis in human alveolar macrophages. We tested the hypothesis that Be stimulates the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which plays a role in Be-induce... |
|
|
Inhibition of normal human lung fibroblast growth by beryllium.
Toxicology 160(1-3) , 119-27, (2001) Inhalation of particulate beryllium (Be) and its compounds causes chronic Be disease (CBD) in a relatively small subset ( approximately 1-6%) of exposed individuals. Hallmarks of this pulmonary disease include increases in several cell types, including lung f... |