(Deamino-Cys1,D-Arg8)-Vasopressin acetate salt
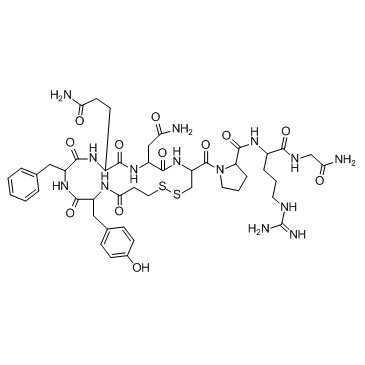
(Deamino-Cys1,D-Arg8)-Vasopressin acetate salt structure
|
Common Name | (Deamino-Cys1,D-Arg8)-Vasopressin acetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16679-58-6 | Molecular Weight | 1069.217 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C46H64N14O12S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Solid lipid particles for oral delivery of peptide and protein drugs III - the effect of fed state conditions on the in vitro release and degradation of desmopressin.
AAPS J. 16(4) , 875-83, (2014) The effect of food intake on the release and degradation of peptide drugs from solid lipid particles is unknown and was therefore investigated in vitro using different fed state media in a lipolysis model. Desmopressin was used as a model peptide and incorpor... |
|
|
Abnormal fluid homeostasis in apelin receptor knockout mice.
J. Endocrinol. 202(3) , 453-62, (2009) The apelinergic system, comprised of apelin and its G protein-coupled receptor (APJ; APLNR as given in MGI Database), is expressed within key regions of the central nervous system associated with arginine vasopressin (AVP) synthesis and release as well as in ... |
|
|
In vitro models for metabolic studies of small peptide hormones in sport drug testing.
J. Pept. Sci. 21(1) , 1-9, (2014) Peptide hormones represent an emerging class of potential doping agents. Detection of their misuse is difficult due to their short half-life in plasma and rapid elimination. Therefore, investigating their metabolism can improve detectability. Unfortunately, p... |
|
|
Integrin-linked kinase regulates tubular aquaporin-2 content and intracellular location: a link between the extracellular matrix and water reabsorption.
FASEB J. 28(8) , 3645-59, (2014) One of the clinical alterations observed in chronic renal disease (CRD) is the impaired urine concentration, known as diabetes insipidus (DI). Tubulointerstitial fibrosis of the kidney is also a pathological finding observed in CRD and involves composition of... |
|
|
Desmopressin improves intestinal functional capillary density and decreases leukocyte activation in experimental endotoxemia.
Microvasc. Res. 97 , 98-104, (2014) Blood flow to the intestine is decreased in sepsis in favor of vital organs resulting in ischemic damage of the gut mucosa. Once the mucosa is damaged, increased translocation of intestinal bacteria to the systemic circulation may occur. This in turn aggravat... |
|
|
Tolvaptan plus pasireotide shows enhanced efficacy in a PKD1 model.
J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26(1) , 39-47, (2015) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a leading cause of ESRD. A central defect associated with ADPKD pathology is elevated levels of 3', 5'-cyclic AMP (cAMP). Compounds such as tolvaptan and pasireotide, which indirectly reduce adenylyl cyc... |
|
|
[Ion-regulating renal function during oral and parenteral potassium loading].
Ross. Fiziol. Zh. Im. I. M. Sechenova 99(3) , 372-82, (2013) Ion-regulating renal function and influence of vasopressin and its analogues on the rate and selectiveness of the urinary potassium excretion were investigated after short-term parenteral and oral potassium loading. In experiments with Wistar rats it was show... |
|
|
Glutamatergic dysregulation in pediatric psychiatric disorders: a systematic review of the magnetic resonance spectroscopy literature.
J. Clin. Psychiatry 75(11) , 1226-41, (2014) As the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, glutamate plays a critical role in normal brain function; thus, its dysregulation could lead to psychopathology in youth. A growing body of literature has investigated the role of glutamate in the pathoph... |
|
|
Toward oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals: an assessment of the gastrointestinal stability of 17 peptide drugs.
Mol. Pharm. 12(3) , 966-73, (2015) A major barrier to successful oral delivery of peptide and protein molecules is their inherent instability in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. The aim of this study was to determine the stability of 17 disparate peptide drugs (insulin, calcitonin, glu... |
|
|
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired von Willebrand syndrome.
Thromb. Res. 130 Suppl 2 , S2-6, (2012) Acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AVWS) is a rare bleeding disorder that is characterized by structural or functional alterations in von Willebrand factor (VWF) caused by a range of lymphoproliferative, myeloproliferative, cardiovascular, autoimmune, and othe... |