Heliotropic acid
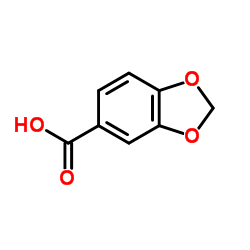
Heliotropic acid structure
|
Common Name | Heliotropic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94-53-1 | Molecular Weight | 166.131 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 324.6±31.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H6O4 | Melting Point | 229-231 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 139.6±18.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
[Study on the bioactive constituents of Piper wallichii].
Zhong Yao Cai 35(1) , 53-6, (2012) To investigate the bioactive constituents in the stem of Piper wallichii.Compounds were separated by column chromatography of silica gel, ODS-A and Sephadex LH-20. Their structures were elucidated based on spectral analysis. DPPH scavenging activity and AchE ... |
|
|
Pattern triggered immunity (PTI) in tobacco: isolation of activated genes suggests role of the phenylpropanoid pathway in inhibition of bacterial pathogens.
PLoS ONE 9(8) , e102869, (2014) Pattern Triggered Immunity (PTI) or Basal Resistance (BR) is a potent, symptomless form of plant resistance. Upon inoculation of a plant with non-pathogens or pathogenicity-mutant bacteria, the induced PTI will prevent bacterial proliferation. Developed PTI i... |
|
|
Free and conjugated benzoic acid in tobacco plants and cell cultures. Induced accumulation upon elicitation of defense responses and role as salicylic acid precursors.
Plant Physiol. 125(1) , 318-28, (2001) Salicylic acid (SA) is a key endogenous component of local and systemic disease resistance in plants. In this study, we investigated the role of benzoic acid (BA) as precursor of SA biosynthesis in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum cv Samsun NN) plants undergoing a ... |
|
|
Biotransformations of propenylbenzenes by an Arthrobacter sp. and its t-anethole blocked mutants.
J. Biotechnol. 105(1-2) , 61-70, (2003) Propenylbenzenes are often used as starting materials in the chemical synthesis of aroma compounds and fine chemicals. In the present study, we demonstrate the ability of an Arthrobacter sp. to transform various structures of propenylbenzenes derived from ess... |
|
|
8-Bromo-7-hydroxyquinoline as a photoremovable protecting group for physiological use: mechanism and scope.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(13) , 4267-76, (2006) Two-photon excitation (2PE) of "caged" biomolecules represents a powerful method to investigate the temporal and spatial relevance of physiological function in real time and on living tissue, because the excitation volume can be restricted to 1 fL. Additional... |
|
|
Chemical inactivation of the cinnamate 4-hydroxylase allows for the accumulation of salicylic acid in elicited cells.
Plant Physiol. 130(2) , 1022-31, (2002) The cinnamate (CA) 4-hydroxylase (C4H) is a cytochrome P450 that catalyzes the second step of the main phenylpropanoid pathway, leading to the synthesis of lignin, pigments, and many defense molecules. Salicylic acid (SA) is an essential trigger of plant dise... |
|
|
Exogenous caffeic acid inhibits the growth and enhances the lignification of the roots of soybean (Glycine max).
J. Plant Physiol. 168(14) , 1627-33, (2011) The allelopathic effect of caffeic acid was tested on root growth, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and peroxidase (POD) activities, hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) accumulation, lignin content and monomeric composition of soybean (Glycine max) roots. We found ... |
|
|
New furanoflavanoids, intestinal alpha-glucosidase inhibitory and free-radical (DPPH) scavenging, activity from antihyperglycemic root extract of Derris indica (Lam.).
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 5170-5, (2009) A bioassay-guided fractionation and chemical examination of antihyperglycemic root extract of Derris indica resulted in isolation and characterization of two new furanoflavanoids (1, 2) along with thirteen known compounds (3-15). Their structures were determi... |
|
|
Accumulation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid in hairy roots of Daucus carota 2: confirming biosynthetic steps through feeding of inhibitors and precursors.
J. Plant Physiol. 166(13) , 1370-80, (2009) Biosynthesis of hydroxybenzoates even at enzymatic level is poorly understood. In this report, effect of feeding of putative biosynthetic precursors and pathway-specific enzyme inhibitors of early phenylpropanoid pathway on p-hydroxybenzoic acid accumulation ... |