Sudan I
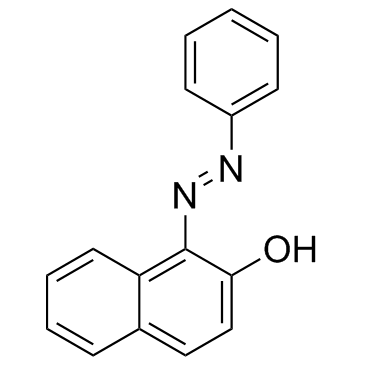
Sudan I structure
|
Common Name | Sudan I | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 842-07-9 | Molecular Weight | 248.279 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 443.7±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H12N2O | Melting Point | 131-133 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 290.2±13.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Development and validation of a confirmatory HPLC method for simultaneous determination of Sudan dyes in animal tissues and eggs.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 48(1) , 63-7, (2010) A simple and sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analytical method for the simultaneous determination of six Sudan dyes (Sudan Red G, Sudan I, Sudan II, Sudan III, Sudan Red 7B, Sudan IV) in animal tissues and eggs was developed. Samples w... |
|
|
Solubilization of two organic dyes by cationic ester-containing gemini surfactants.
J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 376(1) , 112-8, (2012) Solubilization of two different types of organic dyes, Quinizarin with an anthraquinone structure and Sudan I with an azo structure, has been studied in aqueous solutions of a series of cationic gemini surfactants and of a conventional monomeric cationic surf... |
|
|
Accelerated removal of Sudan dye by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in the presence of quinones and humic acids.
World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29(9) , 1723-30, (2013) Although there have been many studies on bacterial removal of soluble azo dyes, much less information is available for biological treatment of water-insoluble azo dyes. The few bacterial species capable of removing Sudan dye generally require a long time to r... |
|
|
Sensitive and fast determination of Sudan dyes in chili powder by partial-filling micellar electrokinetic chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Electrophoresis 33 , 705-12, (2012) A fast and sensitive method for the simultaneous determination of Sudan dyes (I, II, III, and IV) in food samples was developed for the first time using partial filling micellar electrokinectic chromatography-mass spectrometry (MEKC-MS). The use of MEKC was e... |
|
|
An ultrasensitive and selective fluorescence assay for Sudan I and III against the influence of Sudan II and IV.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 42 , 136-40, (2013) We report on an ultrasensitive and selective fluorescence assay for Sudan I and III against the influence of Sudan II and IV based on ligand exchange mechanism. Calcein as a fluorescence indicator and Sudan I-IV as model analytes were employed to investigate ... |
|
|
Evaluation of impact of exposure of Sudan azo dyes and their metabolites on human intestinal bacteria.
Anaerobe 18(4) , 445-53, (2012) Sudan azo dyes are banned for food usage in most countries, but they are illegally used to maintain or enhance the color of food products due to low cost, bright staining, and wide availability of the dyes. In this report, we examined the toxic effects of the... |
|
|
Determination of para red, Sudan dyes, canthaxanthin, and astaxanthin in animal feeds using UPLC.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 48(1) , 22-5, (2010) A simple high-performance liquid chromatography method was developed for quantitative determination of para red, Sudan I, Sudan II, Sudan III, Sudan IV, canthaxanthin, and astaxanthin in feedstuff. The sample was extracted using acetonitrile and cleaned up on... |
|
|
[Determination of four Sudan dyes in chili oil by high performance liquid chromatography with on-line photochemical derivatization and fluorescence detection].
Se Pu 30(6) , 624-9, (2012) A method for the measurement of Sudan I, Sudan II, Sudan III and Sudan B in chili oil using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with on-line photochemical derivatization and fluorescence detection has been developed. The Sudan dyes were separated on... |
|
|
[Selection of the optimal method of extraction and determination of dye Sudan I-IV and Para Red by high-performance liquid chromatography].
Vopr. Pitan. 79(2) , 60-5, (2010) Since 2004 was important the problem of determination of non-food dyes as Sudan I-IV and Para Red. Therefore it was necessary to develop reliable methodologies or adapt existing analytical methods for monitoring the presence of such dyes in food. For this pur... |
|
|
Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of four Sudan dyes in sausage samples.
Analyst 136(12) , 2629-34, (2011) A simple and highly selective molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction (MISPE) combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) was developed for the determination of four Sudan dye (I, II, III, and IV) residues in sausag... |