forchlorfenuron
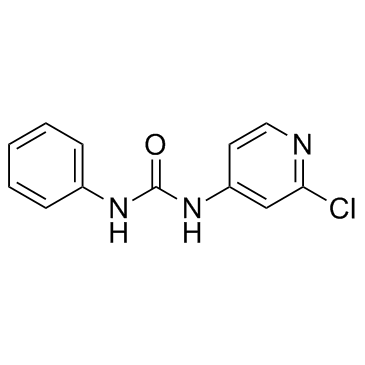
forchlorfenuron structure
|
Common Name | forchlorfenuron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68157-60-8 | Molecular Weight | 247.680 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 426.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10ClN3O | Melting Point | 170-172°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 211.7±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Septins arrange F-actin-containing fibers on the Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion and are required for normal release of the inclusion by extrusion.
MBio 5(5) , e01802-14, (2014) Chlamydia trachomatis is an obligate intracellular human pathogen that grows inside a membranous, cytosolic vacuole termed an inclusion. Septins are a group of 13 GTP-binding proteins that assemble into oligomeric complexes and that can form higher-order fila... |
|
|
Determination of forchlorfenuron in fruits by solid phase or QuECHERS extraction and LC-UV or LC/MS/MS.
J. AOAC Int. 97(3) , 938-41, (2014) Forchlorfenuron, N-(2-chloro-4-pyridinyl)-N'-phenylurea, is a plant growth regulator used to increase the size of kiwifruit, apples, table grapes, and peaches and to promote increased yields of potatoes, rice, and wheat. This study reports the comparison of t... |
|
|
Application of plant growth regulators mitigates chlorotic foliar injury by the black pecan aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae).
Pest Manag. Sci. 66(11) , 1236-42, (2010) Black pecan aphid, Melanocallis caryaefoliae (Davis) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), feeding elicits localized chlorotic injury to pecan foliage [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K Koch] and apparent acceleration of leaf senescence and defoliation. The ability of certa... |
|
|
Chlorophenoxyacetic acid and chloropyridylphenylurea accelerate translocation of photoassimilates to parthenocarpic and seeded fruits of muskmelon (Cucumis melo).
J. Plant Physiol. 168 , 920-926, (2011) We compared the effect of p-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (p-CPA) and 1-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)-3-phenylurea (CPPU) on parthenocarpic and seeded muskmelon (Cucumis melo) fruits in regards to fruit development and the transport of photoassimilates from leaves exposed ... |
|
|
Development and validation of a direct competitive monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for the sensitive and selective analysis of the phytoregulator forchlorfenuron.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 403(7) , 2019-26, (2012) Forchlorfenuron is a synthetic phytohormone with cytokinin-like activity used worldwide as a plant growth regulator to increase fruit size in a number of crops, mostly in kiwifruit and grape vines. A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay... |
|
|
Cloning of gibberellin 3 beta-hydroxylase cDNA and analysis of endogenous gibberellins in the developing seeds in watermelon.
Plant Cell Physiol. 43(2) , 152-8, (2002) We have isolated Cv3h, a cDNA clone from the developing seeds of watermelon, and have demonstrated significant amino acid homology with gibberellin (GA) 3 beta-hydroxylases. This cDNA clone was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion protein that oxidized G... |
|
|
Determination of forchlorfenuron residues in watermelon by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography.
J. AOAC Int. 89(6) , 1635-40, (2006) A method using solid-phase extraction for cleanup, followed by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection (HPLC/UV), was developed for the determination of forchlorfenuron residues in watermelon. The pesticide is extracted from the samp... |
|
|
Urea derivatives on the move: cytokinin-like activity and adventitious rooting enhancement depend on chemical structure.
Plant Biol. (Stuttg.) 11(3) , 262-72, (2009) Urea derivatives are synthetic compounds, some of which have proved to be positive regulators of cell division and differentiation. N-phenyl-N'-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)urea (forchlorofenuron, CPPU) and N-phenyl-N'-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl)urea (thidiazuron, TDZ), w... |
|
|
Spatio-temporal changes in cell division, endoreduplication and expression of cell cycle-related genes in pollinated and plant growth substances-treated ovaries of cucumber.
Plant Biol. (Stuttg.) 12(1) , 98-107, (2010) We investigated the temporal and spatial changes in cell division, endoreduplication and expression of cell cycle-related genes in developing cucumber fruits at 0-20 days after anthesis (DAA). Cell division was intense at 0-4 DAA and then decreased until to 8... |
|
|
Cellular requirements for the small molecule forchlorfenuron to stabilize the septin cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeleton (Hoboken.) 67(6) , 383-99, (2010) The septins are filament-forming, GTP-binding proteins that are conserved from yeast to humans. Septins assemble into higher-order structures such as rings, bars, and gauzes with diverse functions including serving as membrane diffusion barriers and scaffolds... |