DIETHYLUMBELLIFERYL PHOSPHATE
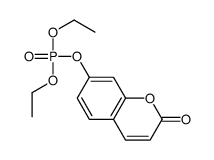
DIETHYLUMBELLIFERYL PHOSPHATE structure
|
Common Name | DIETHYLUMBELLIFERYL PHOSPHATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 897-83-6 | Molecular Weight | 298.22800 | |
| Density | 1.272g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 408.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H15O6P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 214.3ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Fungal recognition enhances mannose receptor shedding through dectin-1 engagement.
J. Biol. Chem. 286(10) , 7822-9, (2011) The mannose receptor (MR) is an endocytic type I membrane molecule with a broad ligand specificity that is involved in both hemostasis and pathogen recognition. Membrane-anchored MR is cleaved by a metalloproteinase into functional soluble MR (sMR) composed o... |
|
|
AMPK activation promotes lipid droplet dispersion on detyrosinated microtubules to increase mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 7176, (2015) Lipid droplets (LDs) are intracellular organelles that provide fatty acids (FAs) to cellular processes including synthesis of membranes and production of metabolic energy. While known to move bidirectionally along microtubules (MTs), the role of LD motion and... |
|
|
Defective triglyceride biosynthesis in CETP-deficient SW872 cells.
J. Lipid Res. 56 , 1669-78, (2015) We previously reported that reducing the expression of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) disrupts cholesterol homeostasis in SW872 cells and causes an ∼50% reduction in TG. The causes of this reduced TG content, investigated here, could not be attribu... |
|
|
Influence of an alkalizing supplement on markers of endurance performance using a double-blind placebo-controlled design.
J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 9 , 8, (2012) Previous research has shown that ingestion of substances that enhance the body's hydrogen ion buffering capacity during high intensity exercise can improve exercise performance. The present study aimed to determine whether the chronic ingestion of an alkalizi... |
|
|
High-capacity selective uptake of cholesteryl ester from native LDL during macrophage foam cell formation.
J. Lipid Res. 53 , 2081-91, (2012) Macrophage foam cells are a defining pathologic feature of atherosclerotic lesions. Recent studies have demonstrated that at high concentrations associated with hypercholesterolemia, native LDL induces macrophage lipid accumulation. LDL particles are taken up... |
|
|
Factors underlying the variability of lipid droplet fluorescence in MA-10 Leydig tumor cells.
Cytometry 17(2) , 151-8, (1994) Neutral lipids accumulate in cellular lipid droplets. These droplets vary remarkably in number and amount between cells. In the present studies, the variability in lipid content was quantified by comparing the coefficient of variation of fluorescence histogra... |
|
|
Evidence that a neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase is responsible for the extralysosomal hydrolysis of high-density lipoprotein cholesteryl ester in rat hepatoma cells (Fu5AH).
J. Cell Physiol. 157(1) , 164-8, (1993) Diethylumbelliferyl phosphate (UBP) has been shown to inhibit the neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase activity responsible for hydrolysis of cellular lipid droplet cholesteryl ester (Harrison et al., 1990). The potential for (UBP) to inhibit uptake and hydrol... |
|
|
Diethylumbelliferyl phosphate inhibits steroidogenesis by interfering with a long-lived factor acting between protein kinase A activation and induction of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR).
Eur. J. Biochem. 234(2) , 680-5, (1995) Diethylumbelliferyl phosphate (DEUP) is an organophosphate cholesteryl ester hydrolase inhibitor that blocks steroidogenesis mainly by preventing cholesterol transport into the mitochondria of steroidogenic cells. In the present study, we show that DEUP block... |
|
|
A rapid oxygen exchange on prostaglandins in plasma represents plasma esterase activity that is inhibited by diethylumbelliferyl phosphate with high affinity.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 26(20) , 2472-6, (2012) Fatty acids (FA) labeled with (18) O at the carboxyl group, including oxidized species (FA(18) O), are a useful, low-cost, and easy to prepare tool for quantitative and qualitative mass spectrometry (MS) analysis in biological systems. In addition, they are u... |