D-Erythrose
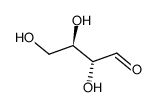
D-Erythrose structure
|
Common Name | D-Erythrose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 583-50-6 | Molecular Weight | 120.10400 | |
| Density | 1.698 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 290.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8O4 | Melting Point | <25℃ | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 129.5ºC | |
|
Biosynthesis of l-Sorbose and l-Psicose Based on C-C Bond Formation Catalyzed by Aldolases in an Engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum Strain.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 , 4284-94, (2015) The property of loose stereochemical control at aldol products from aldolases helped to synthesize multiple polyhydroxylated compounds with nonnatural stereoconfiguration. In this study, we discovered for the first time that some fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldo... |
|
|
Identification of novel thermostable taurine-pyruvate transaminase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans for chiral amine synthesis.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100 , 3101-11, (2016) ω-Transaminases (ω-TAs) are one of the most popular candidate enzymes in the biosynthesis of chiral amines. Determination of yet unidentified ω-TAs is important to broaden their potential for synthetic application. Taurine-pyruvate TA (TPTA, EC 2.6.1.77) is a... |
|
|
Conformational study of the open-chain and furanose structures of D-erythrose and D-threose.
Carbohydr. Res. 358 , 96-105, (2012) The potential energy surfaces for the different configurations of the D-erythrose and D-threose (open-chain, α- and β-furanoses) have been studied in order to find the most stable structures in the gas phase. For that purpose, a large number of initial struct... |
|
|
Computational study of mutarotation in erythrose and threose.
Carbohydr. Res. 346(18) , 2933-9, (2011) For the first time the mutarotation mechanism of furanose rings has been investigated, with and without solvent. The transformations from open-chain furanose to D-erythrose and D-threose have been studied at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) and G3MP2B3 levels, in vacuum a... |
|
|
Carbohydrate carbonyl mobility--the key process in the formation of alpha-dicarbonyl intermediates.
Carbohydr. Res. 339 , 1609-1618, (2004) Covalently cross-linked proteins are among the major modifications caused by the advanced Maillard reaction. In the present study, the formation pathway of the dideoxyosone N6-(2,3-dihydroxy-5,6-dioxohexyl)-L-lysine is shown. To elucidate the formation of thi... |
|
|
Growth of organic microspherules in sugar-ammonia reactions.
Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 35 , 523-536, (2005) Reaction of small sugars of less than four carbons with ammonia in water yielded organic microspherules generally less than ten microns in size. The time course of microspherule growth was examined for the D-erythrose-ammonia reaction that yielded microspheru... |
|
|
Microspherules from sugars in the absence of nitrogen.
Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 41 , 17-22, (2011) Reactions of short sugars under mild, plausibly prebiotic conditions yield organic microspherules that may have played a role in prebiotic chemistry as primitive reaction vessels. It has been widely thought that nitrogen chemistry, in particular Amadori rearr... |
|
|
Characterization of erythrose reductases from filamentous fungi.
AMB Express 3 , 43, (2013) Proteins with putative erythrose reductase activity have been identified in the filamentous fungi Trichoderma reesei, Aspergillus niger, and Fusarium graminearum by in silico analysis. The proteins found in T. reesei and A. niger had earlier been characterize... |
|
|
Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a novel erythrose reductase from Candida magnoliae JH110.
Microb. Cell Fact. 9 , 43, (2010) Erythrose reductase (ER) catalyzes the final step of erythritol production, which is reducing erythrose to erythritol using NAD(P)H as a cofactor. ER has gained interest because of its importance in the production of erythritol, which has extremely low digest... |