sits
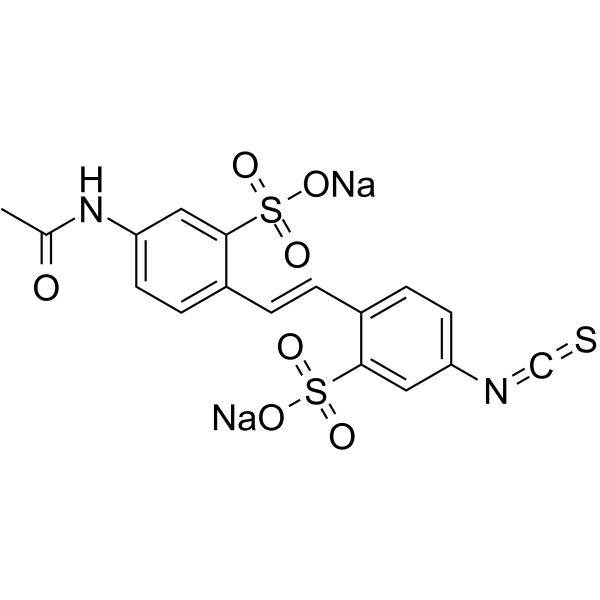
sits structure
|
Common Name | sits | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51023-76-8 | Molecular Weight | 498.461 | |
| Density | 1.52g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H12N2Na2O7S3 | Melting Point | >300ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Excitation of rat sympathetic neurons via M1 muscarinic receptors independently of Kv7 channels.
Pflugers Arch. 466(12) , 2289-303, (2014) The slow cholinergic transmission in autonomic ganglia is known to be mediated by an inhibition of Kv7 channels via M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. However, in the present experiments using primary cultures of rat superior cervical ganglion neurons, th... |
|
|
Tuning the reactivity in classic low-spin d6 rhenium(I) tricarbonyl radiopharmaceutical synthon by selective bidentate ligand variation (L,L'-Bid; L,L'= N,N', N,O, and O,O' donor atom sets) in fac-[Re(CO)3(L,L'-Bid)(MeOH)]n complexes.
Inorg. Chem. 50(24) , 12486-98, (2011) A range of fac-[Re(CO)(3)(L,L'-Bid)(H(2)O)](n) (L,L'-Bid = neutral or monoanionic bidentate ligands with varied L,L' donor atoms, N,N', N,O, or O,O': 1,10-phenanthroline, 2,2'-bipydine, 2-picolinate, 2-quinolinate, 2,4-dipicolinate, 2,4-diquinolinate, tribrom... |
|
|
Mechanisms of chloride in cardiomyocyte anoxia-reoxygenation injury: the involvement of oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 355(1-2) , 201-9, (2011) During anoxia/reoxygenation (A/R) injury, intracellular chloride ion concentration ([Cl(-)](i)) homeostasis may play a role in maintaining the normal physiological function of cardiomyocytes. Various chloride transport systems could have influenced the concen... |
|
|
[Glucose-6-phosphatase from nuclear envelope in rat liver].
Invest. Clin. 49(2) , 169-80, (2008) Nuclear envelope (NE) and microsomal glucosa-6-phosphatase (G-6-Pase) activities were compared. Intact microsomes were unable to hydrolyze mannose-6-phosphate (M-6-P), on the other hand, intact NE hydrolyzes this substrate. Galactose-6-phosphate showed to be ... |
|
|
Modulation of butyrate transport in Caco-2 cells.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 379(4) , 325-36, (2009) The aim of this study was to investigate the putative influence of some pharmacological agents and drugs of abuse upon the apical uptake of butyrate (BT) into Caco-2 cells. The apical uptake of (14)C-BT by Caco-2 cells was (1) time and concentration dependent... |
|
|
Initiation of motility by steelhead (Oncorhynchus mykiss) sperm: membrane ion exchangers and pH sensitivity.
Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. Mol. Integr. Physiol. 151(4) , 651-6, (2008) Initiation of motility in salmonid sperm is sensitive to the pH of the extracellular medium, however, the basis of this sensitivity is not clear. Sperm incubated in an immobilization buffer (SI) at low pH ( approximately 7.1-7.2) become motile when diluted wi... |
|
|
Lysosomal chymotrypsin B potentiates apoptosis via cleavage of Bid.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67(15) , 2665-78, (2010) We have reported that chymotrypsin B (CtrB) is not just a digestive enzyme but is also stored in lysosomes. Herein, we demonstrated a broad distribution of CtrB and explored the involvement of CtrB in apoptosis. Exposure of RH-35 cells to H(2)O(2) or palmitat... |
|
|
Agonist-dependent potentiation of vanilloid receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 function by stilbene derivatives.
Mol. Pharmacol. 81(5) , 689-700, (2012) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) is a nonselective cation channel activated by capsaicin, low pH, and noxious heat and plays a key role in nociception. Understanding mechanisms for functional modulation of TRPV1 has important implications... |
|
|
Glutathione- and thioredoxin-related enzymes are modulated by sulfur-containing chemopreventive agents.
Biol. Chem. 388(10) , 1069-81, (2007) We studied the effects of sulfur-containing chemopreventive agents, including allyl sulfides and isothiocyanates, on human redox networks. Isothiocyanates inhibited isolated redox-active enzymes in a time- and dose-dependent manner. As shown for the most acti... |
|
|
Volume-activated chloride channels in mice Leydig cells.
Pflugers Arch. 457(2) , 493-504, (2008) Production and secretion of testosterone in Leydig cells are mainly controlled by the luteinizing hormone (LH). Biochemical evidences suggest that the activity of Cl(-) ions can modulate the steroidogenic process, but the specific ion channels involved are no... |