Lisinopril diydrate
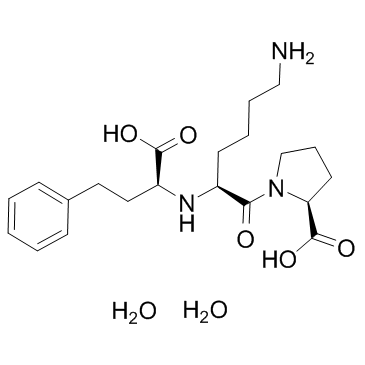
Lisinopril diydrate structure
|
Common Name | Lisinopril diydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 83915-83-7 | Molecular Weight | 441.52 | |
| Density | 1.251 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 666.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H35N3O7 | Melting Point | 160ºC (Decomposes) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 356.9ºC | |
|
Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory tripeptide from enzymatic hydrolysis of soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) egg white: in vitro, in vivo, and in silico study.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(50) , 12178-85, (2014) In this study, a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory tripeptide (IVR) was isolated and identified from unfertilized soft-shelled turtle egg white (SSTEW). The IC50 value of IVR was measured in vitro as low as 0.81 ± 0.03 μM, and its inhibitio... |
|
|
Effects of a fixed-dose combination strategy on adherence and risk factors in patients with or at high risk of CVD: the UMPIRE randomized clinical trial.
JAMA 310(9) , 918-29, (2013) Most patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) do not take recommended medications long-term. The use of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) improves adherence in several clinical areas. Previous trials of cardiovascular FDCs have assessed short-term effects comp... |
|
|
Effects of a domain-selective ACE inhibitor in a mouse model of chronic angiotensin II-dependent hypertension.
Clin. Sci. 127(1) , 57-63, (2014) The somatic isozyme of ACE (angiotensin I-converting enzyme) comprises two distinct zinc-dependent catalytic domains with different substrate specificities for angiotensin I (cleaved selectively by the C-domain) and bradykinin (cleaved equally efficiently by ... |
|
|
Effects of a new SGLT2 inhibitor, luseogliflozin, on diabetic nephropathy in T2DN rats.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 345(3) , 464-72, (2013) This study examined the effect of long-term control of hyperglycemia with a new sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, luseogliflozin, given alone or in combination with lisinopril on the progression of renal injury in the T2DN rat model of type 2 diabetic... |
|
|
Time of administration important? Morning versus evening dosing of valsartan.
J. Hypertens. 33(2) , 385-92, (2014) Studies suggest that bedtime dosing of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker shows a more sustained and consistent 24-h antihypertensive profile, including greater night-time blood pressure (BP) reduction. We compare... |
|
|
The Effect of Formulation Excipients and Thermal Treatment on the Release Properties of Lisinopril Spheres and Tablets.
Biomed Res. Int. 2015 , 423615, (2015) Multiparticulate systems are used in the development of controlled release systems. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of the wax level, the type of excipient, and the exposure of the tablets to thermal treatment on drug release. Spheres ... |
|
|
Hyperoxia downregulates angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 in human fetal lung fibroblasts.
Pediatr. Res. 77(5) , 656-62, (2015) Angiotensin (ANG) II is involved in experimental hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) degrades ANG II and is thus protective, but is downregulated in adult human and experimental lung fibrosis. Hyperoxia is a known cause of... |
|
|
Primacy of angiotensin converting enzyme in angiotensin-(1-12) metabolism.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 305(5) , H644-50, (2013) Angiotensin-(1-12) [ANG-(1-12)], a new member of the renin-angiotensin system, is recognized as a renin independent precursor for ANG II. However, the processing of ANG-(1-12) in the circulation in vivo is not fully established. We examined the effect of angi... |
|
|
Surface plasmon resonance analysis of the binding mechanism of pharmacological and peptidic inhibitors to human somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme.
Biochemistry 52(48) , 8722-31, (2013) Somatic angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) possesses two catalytic domains and plays a major role in the regulation of blood pressure, thus representing a therapeutic target for the treatment of hypertension. We present a comprehensive surface plasmon reso... |
|
|
N- versus C-domain selectivity of catalytic inactivation of human angiotensin converting enzyme by lisinopril-coupled transition metal chelates.
J. Med. Chem. 56(24) , 9826-36, (2013) The N- and C-terminal domains of human somatic angiotensin I converting enzyme (sACE-1) demonstrate distinct physiological functions, with resulting interest in the development of domain-selective inhibitors for specific therapeutic applications. Herein, the ... |