Disodium 4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl phosphate
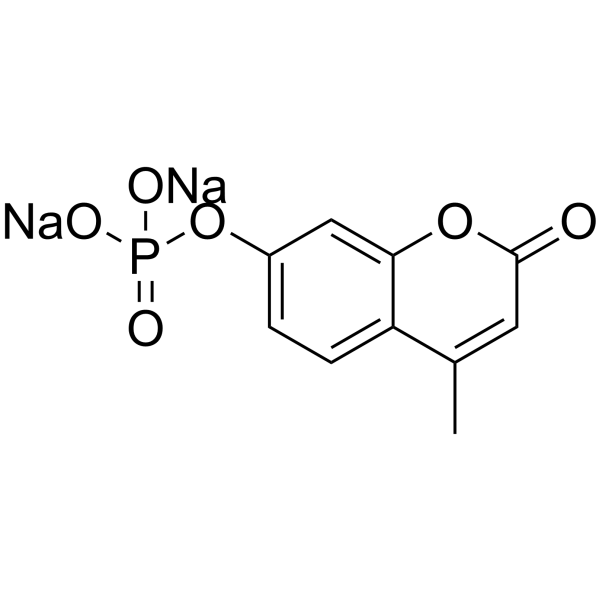
Disodium 4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Disodium 4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22919-26-2 | Molecular Weight | 300.112 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 511.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7Na2O6P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 263.1ºC | |
|
Sequential release of nanoparticle payloads from ultrasonically burstable capsules.
Biomaterials 75 , 91-101, (2015) In many biomedical contexts ranging from chemotherapy to tissue engineering, it is beneficial to sequentially present bioactive payloads. Explicit control over the timing and dose of these presentations is highly desirable. Here, we present a capsule-based de... |
|
|
Surface hydroxyl groups direct cellular response on amorphous and anatase TiO2 nanodots.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 123 , 68-74, (2014) In this study, we investigated the differences between amorphous and anatase TiO2 at the biomolecular level which could explain differences in the osteoblast response on these surfaces. The number of surface hydroxyl groups in the TiOHT form on amorphous and ... |
|
|
The metabolism of lysophosphatidic acids by allelic variants of human soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 30(1) , 75-81, (2015) Lysophosphatidic acids (LPAs) are phospholipids which have many physiological and pathophysiological functions. The human soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) plays a role in the metabolism of xenobiotics through its metabolism of aromatic hydrocarbon epoxides suc... |
|
|
Hybrid flagellin as a T cell independent vaccine scaffold.
BMC Biotechnol. 15 , 71, (2015) To extend the potency of vaccines against infectious diseases, vaccines should be able to exploit multiple arms of the immune system. One component of the immune system that is under-used in vaccine design is the subset of B cells known to be capable of respo... |
|
|
Aptamer-based detection of disease biomarkers in mouse models for chagas drug discovery.
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(1) , e3451, (2015) Drug discovery initiatives, aimed at Chagas treatment, have been hampered by the lack of standardized drug screening protocols and the absence of simple pre-clinical assays to evaluate treatment efficacy in animal models. In this study, we used a simple Enzym... |
|
|
A single-molecule digital enzyme assay using alkaline phosphatase with a cumarin-based fluorogenic substrate.
Analyst 140 , 5065-73, (2015) Digitalization of fluorogenic enzymatic assays through the use of femtoliter chamber array technology is an emerging approach to realizing highly quantitative bioassays with single-molecule sensitivity. However, only a few digital fluorogenic enzyme assays ha... |
|
|
Fluorescence enhancement aided by metal ion displacement.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 80 , 237-42, (2016) Immunosensors are one of the most common platform used in clinical laboratories, in particular the class based on Enzyme Linked Fluorescent Assays (ELFA) takes advantage of the amplification step of the enzyme, usually the alkaline phosphatase, that catalyzes... |
|
|
Application of intracellular alkaline phosphatase activity measurement in detection of neutrophil adherence in vitro.
Mediators Inflamm. 2006(4) , 19307, (2006) We have proposed the use of the fluorimetric method with 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate (4-MUP) specific substrate for the alkaline phosphatase determination in the neutrophil adhesion assay. We provide evidence that the endogenous neutrophil alkaline phospha... |
|
|
T3D-959: A Multi-Faceted Disease Remedial Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.
J. Alzheimers Dis. 51 , 123-38, (2016) T3D-959, a dual PPAR-δ/PPAR γ nuclear receptor agonist and former diabetes drug candidate, has been repositioned as an Alzheimer's disease (AD)-modifying therapy.This study examines the effectiveness and mechanisms of T3D-959's therapeutic effects using in vi... |
|
|
Role of material-driven fibronectin fibrillogenesis in protein remodeling.
Biores. Open Access 2 , 364-73, (2013) Protein remodeling at the cell-material interface is an important phenomenon that should be incorporated into the design of advanced biomaterials for tissue engineering. In this work, we address the relationship between fibronectin (FN) activity at the materi... |