| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
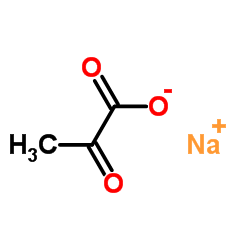 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
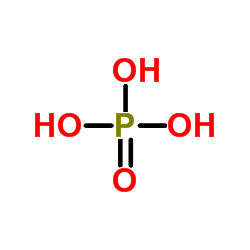 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Aqueous ammonia
CAS:1336-21-6 |
|
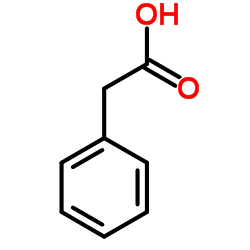 |
Phenylacetic acid
CAS:103-82-2 |
|
 |
Terabutyl titanate
CAS:5593-70-4 |
|
 |
2-Pyrrolidinone
CAS:616-45-5 |
|
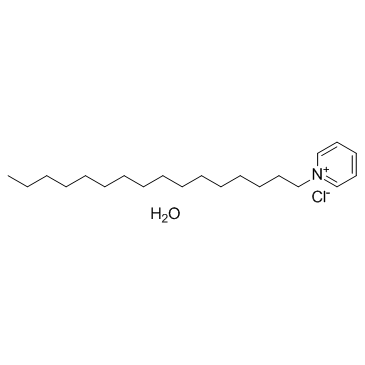 |
Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate
CAS:6004-24-6 |
|
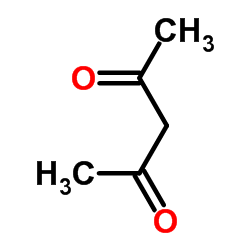 |
2,4-Pentandione
CAS:123-54-6 |