Dimaprit dihydrochloride
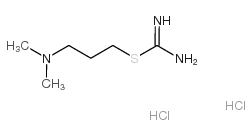
Dimaprit dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Dimaprit dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23256-33-9 | Molecular Weight | 234.19000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H17Cl2N3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Endothelial CD99 signals through soluble adenylyl cyclase and PKA to regulate leukocyte transendothelial migration.
J. Exp. Med. 212 , 1021-41, (2015) CD99 is a critical regulator of leukocyte transendothelial migration (TEM). How CD99 signals during this process remains unknown. We show that during TEM, endothelial cell (EC) CD99 activates protein kinase A (PKA) via a signaling complex formed with the lysi... |
|
|
Involvement of histaminergic inputs in the jaw-closing reflex arc.
J. Neurophysiol. 113 , 3720-35, (2015) Histamine receptors are densely expressed in the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MesV) and trigeminal motor nucleus. However, little is known about the functional roles of neuronal histamine in controlling oral-motor activity. Thus, using the whole-cell rec... |
|
|
Analysis of the histamine H2-receptor in human monocytes.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 92(2) , 369-79, (2014) Histamine receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Canonically, the histamine H2-receptor (H2R) couples to Gs-proteins and activates adenylyl cyclases (ACs) with subsequent adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) generation. Recently, the classi... |
|
|
Role of the thalamic submedius nucleus histamine H1 and H 2 and opioid receptors in modulation of formalin-induced orofacial pain in rats.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 388 , 1089-96, (2015) Histamine and opioid systems are involved in supraspinal modulation of pain. In this study, we investigated the effects of separate and combined microinjections of agonists and antagonists of histamine H1 and H2 and opioid receptors into the thalamic submediu... |
|
|
Activation of adenosine low-affinity A3 receptors inhibits the enteric short interplexus neural circuit triggered by histamine.
Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 297(6) , G1147-62, (2009) We tested the novel hypothesis that endogenous adenosine (eADO) activates low-affinity A3 receptors in a model of neurogenic diarrhea in the guinea pig colon. Dimaprit activation of H2 receptors was used to trigger a cyclic coordinated response of contraction... |
|
|
CCL22/Macrophage-derived Chemokine Expression in Apolipoprotein E-deficient Mice and Effects of Histamine in the Setting of Atherosclerosis.
J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 22 , 599-609, (2015) Macrophage-derived chemokine (CCL22) is a member of the CC-family of chemokines synthesized by monocyte-derived macrophages. Previous studies have reported a relationship between CCL22 and atherosclerosis and the role of histamine in this pathway. Histamine n... |
|
|
Histamine excites neonatal rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vitro via activation of H1 receptors.
J. Neurophysiol. 95(4) , 2492-500, (2006) The role of histamine in regulating excitability of sympathetic preganglionic neurons (SPNs) and the expression of histamine receptor mRNA in SPNs was investigated using whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiological recording techniques combined with single-cel... |
|
|
Suppression of ischaemia-induced cytokine release by dimaprit and amelioration of liver injury in rats.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 102(4) , 394-8, (2008) Inflammatory reactions play an important role in ischaemia/reperfusion injury in various organs. Since histamine H(4) action has been shown to prevent the development of ischaemia/reperfusion liver injury, we examined the effects of dimaprit, a histamine H(2)... |
|
|
Loss of histaminergic modulation of thermoregulation and energy homeostasis in obese mice.
Neuroscience 217 , 84-95, (2012) Histamine acts centrally to increase energy expenditure and reduce body weight by mechanisms not fully understood. It has been suggested that in the obese state hypothalamic histamine signaling is altered. Previous studies have also shown that histamine actin... |
|
|
Blockade of brain histamine metabolism alters methamphetamine-induced expression pattern of stereotypy in mice via histamine H1 receptors.
Neuroscience 147(3) , 765-77, (2007) The administration of methamphetamine (METH, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) to male ICR mice induced stereotyped behavior consisting of nail and/or wood chip biting (86.0%), continuous sniffing (12.0%), head bobbing (1.1%), and circling (1.0%) during the observation period ... |