12-Aminododecanoic acid
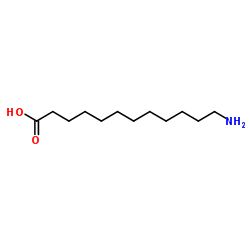
12-Aminododecanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 12-Aminododecanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 693-57-2 | Molecular Weight | 215.33 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 349.7±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H25NO2 | Melting Point | 185-187 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 165.3±20.4 °C | |
|
Structure-activity relationship study on a simple cationic peptide motif for cellular delivery of antisense peptide nucleic acid.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 6741-9, (2005) Improving cellular uptake and biodistribution remains one of the major obstacles for a successful and broad application of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) as antisense therapeutics. Recently, we reported the identification and functional characterization of an a... |
|
|
Development of 68Ga-labeled fatty acids for their potential use in cardiac metabolic imaging.
J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 57(7) , 463-9, (2014) While [(11)C]palmitate continues to be a promising tracer for cardiovascular Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging, unfavourable logistics due to the short half-life of (11)C (20 min) and cumbersome labeling methodologies are the major impediments that l... |
|
|
Multi-dye theranostic nanoparticle platform for bioimaging and cancer therapy.
Int. J. Nanomedicine 7 , 2739-50, (2012) Theranostic nanomaterials composed of fluorescent and photothermal agents can both image and provide a method of disease treatment in clinical oncology. For in vivo use, the near-infrared (NIR) window has been the focus of the majority of studies, because of ... |
|
|
Chemoenzymatic synthesis and chemical recycling of poly(ester-urethane)s.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12 , 5490-507, (2011) Novel poly(ester-urethane)s were prepared by a synthetic route using a lipase that avoids the use of hazardous diisocyanate. The urethane linkage was formed by the reaction of phenyl carbonate with amino acids and amino alcohols that produced urethane-contain... |
|
|
The influence of montmorillonite clay reinforcement on the performance of a glass ionomer restorative.
J. Dent. 34(10) , 802-10, (2006) A pristine calcium montmorillonite (Ca-MMT) and an organically modified 12-amino-dodecanoicacid treated montmorillonite (ADA-MMT) clay were evaluated to determine the reinforcement effect on the performance of a glass ionomer (GI) restorative ChemFil Superior... |
|
|
The impact of montmorillonite clay addition on the in vitro wear resistance of a glass-ionomer restorative.
J. Dent. 35(4) , 309-17, (2007) The in vitro wear resistance of a glass-ionomer (GI) restorative ChemFil Superior (Dentsply DeTrey, Kanstanz, Germany) reinforced with either a pristine calcium montmorillonite (Ca-MMT) or an organically modified 12-amino-dodecanoicacid treated montmorillonit... |
|
|
The role of surface charge on the uptake and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with osteoblast cells.
Nanotechnology 22(10) , 105708, (2011) The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanoparticles with different surface charges on the cellular uptake behavior and in vitro cell viability and proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cell lines (osteoblast). The nanoparticles' su... |
|
|
Synthesis of fluorescent and radiolabeled analogues of phosphatidic acid
Chem. Phys. Lipids 36 , 197, (1985) Procedures for the synthesis of fluorescent and radiolabeled analogues of phosphatidic acid are described. The fluorophore 7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD) was coupled to 6-aminocaproic acid and 12-aminododecanoic acid by reaction of NBD-chloride with the... |
|
|
Galactosylceramide containing omega-amino-fatty acids: preparation, characterization, and sulfotransferase acceptor.
J. Lipid Res. 33(8) , 1227-32, (1992) For preparation of an affinity ligand, an N-fatty acyl moiety of galactosylceramide (GalCer) was chemically replaced with omega-amino-fatty acid including amino-n-hexanoic acid or amino-n-dodecanoic acid to obtain omega-aminoGalCer. For the synthesis of the c... |
|
|
Kinetic mechanism of human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase.
Biochemistry 39(35) , 10720-9, (2000) Formaldehyde, a major industrial chemical, is classified as a carcinogen because of its high reactivity with DNA. It is inactivated by oxidative metabolism to formate in humans by glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase. This NAD(+)-dependent enzyme ... |