Xanthohumol
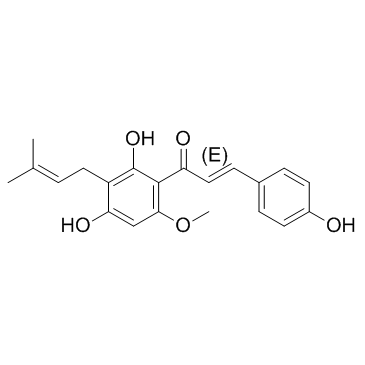
Xanthohumol structure
|
Common Name | Xanthohumol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6754-58-1 | Molecular Weight | 354.396 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 576.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O5 | Melting Point | 157-159ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 203.4±23.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Xanthohumol modulates inflammation, oxidative stress, and angiogenesis in type 1 diabetic rat skin wound healing.
J. Nat. Prod. 76(11) , 2047-53, (2013) Type 1 diabetes mellitus is responsible for metabolic dysfunction, accompanied by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelium dysfunction, and is often associated with impaired wound healing. Phenol-rich food improves vascular function, contributi... |
|
|
Protective effects of arachidonic acid against palmitic acid-mediated lipotoxicity in HIT-T15 cells.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 364(1-2) , 19-28, (2012) Saturated fatty acids have been considered major contributing factors in type 2 diabetes, whereas unsaturated fatty acids have beneficial effects for preventing the development of diabetes. However, the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids in pancreatic β c... |
|
|
Search method for inhibitors of Staphyloxanthin production by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35(1) , 48-53, (2012) Staphyloxanthin, a yellow pigment produced by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), is a virulent factor escaping from the host immune system. A new screening method for inhibitors of staphyloxanthin production by MRSA was established using pape... |
|
|
Interaction of prenylated chalcones and flavanones from common hop with phosphatidylcholine model membranes.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1838(1 Pt B) , 173-84, (2014) Common hop (Humulus lupulus) constitutes a source of numerous prenylated chalcones such as xanthohumol (XH) and flavanones such as 8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN) and isoxanthohumol (IXH). Range of their biological activities includes estrogenic, anti-inflammatory,... |
|
|
Regulation of intracellular pH by glycosaminoglycans.
J. Cell Physiol. 228(10) , 2071-5, (2013) The intracellular pH is regulated by a delicate balance of ion distribution across the plasma membrane and the physico-chemical properties of intra- and extracellular components. We analyzed the effects of glycosaminoglycans on the intracellular pH of fibrobl... |
|
|
Xanthohumol induces phase II enzymes via Nrf2 in human hepatocytes in vitro.
Toxicol. In Vitro 27(1) , 149-56, (2013) The aim of this study was to investigate whether xanthohumol may exert chemoprotective activity through the modulation of the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway in immortalized normal THLE-2 hepatocytes and a hepatocellular carcinoma H... |
|
|
Pitfalls in cell culture work with xanthohumol.
Pharmazie 67(1) , 91-4, (2012) Xanthohumol, the most abundant prenylated chalcone in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) cones, is well known to exert several promising pharmacological activities in vitro and in vivo. Among these, the chemopreventive, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects are pro... |
|
|
A metabolomics-driven elucidation of the anti-obesity mechanisms of xanthohumol.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(26) , 19000-13, (2013) Mild, mitochondrial uncoupling increases energy expenditure and can reduce the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Activation of cellular, adaptive stress response pathways can result in an enhanced capacity to reduce oxidative damage. Together, thes... |
|
|
Xanthohumol impairs human prostate cancer cell growth and invasion and diminishes the incidence and progression of advanced tumors in TRAMP mice.
Mol. Med. 18 , 1292-302, (2012) Despite recent advances in understanding the biological basis of prostate cancer, management of the disease, especially in the phase resistant to androgen ablation, remains a significant challenge. The long latency and high incidence of prostate carcinogenesi... |
|
|
Xanthohumol suppresses inflammatory response to warm ischemia-reperfusion induced liver injury.
Exp. Mol. Pathol. 94(1) , 10-6, (2013) Liver ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) leads to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which cause hepatic injury and initiate an inflammatory response, which is a critical problem after liver surgery and transplantation. Xanthohumol, the major prenylated chal... |