Rhodblock 3
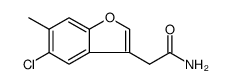
Rhodblock 3 structure
|
Common Name | Rhodblock 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 879564-86-0 | Molecular Weight | 223.65600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H10ClNO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Palmitoylethanolamide controls reactive gliosis and exerts neuroprotective functions in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.
Cell Death Dis. 5 , e1419, (2014) Given the complex heterogeneity of pathological changes occurring in Alzheimer's disease (AD), any therapeutic effort absolutely requires a multi-targeted approach, because attempts addressing only a single event may result ineffective. Palmitoylethanolamide ... |
|
|
Apollon/Bruce is upregulated by Humanin.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 397(1-2) , 147-55, (2014) Humanin, a short bioactive peptide, inhibits a variety of cell deaths. Humanin-mediated inhibition of neuronal cell death, caused by an Alzheimer's disease (AD)-linked mutant gene occurs via binding of Humanin to its heterotrimeric Humanin receptor (htHNR), w... |
|
|
Neurotransmitter Systems in a Mild Blast Traumatic Brain Injury Model: Catecholamines and Serotonin.
J. Neurotrauma 32 , 1190-9, (2015) Exposure to improvised explosive devices can result in a unique form of traumatic brain injury--blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI). At the mild end of the spectrum (mild bTBI [mbTBI]), there are cognitive and mood disturbances. Similar symptoms have ... |
|
|
Phosphoregulatory protein 14-3-3 facilitates SAC1 transport from the endoplasmic reticulum.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , E3199-206, (2015) Most secretory cargo proteins in eukaryotes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and actively exported in membrane-bound vesicles that are formed by the cytosolic coat protein complex II (COPII). COPII proteins are assisted by a variety of cargo-speci... |
|
|
Knock-in of human BACE1 cleaves murine APP and reiterates Alzheimer-like phenotypes.
J. Neurosci. 34(32) , 10710-28, (2014) Key neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are elevated levels of amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) species generated via amyloid precursor protein (APP) endoproteolysis and cleavage by the rate-limiting β-site enzyme 1 (BACE1). Because rodents do not d... |
|
|
The amyloid precursor protein (APP) intracellular domain regulates translation of p44, a short isoform of p53, through an IRES-dependent mechanism.
Neurobiol. Aging 36 , 2725-36, (2015) p44 is a short isoform of the tumor suppressor protein p53 that is regulated in an age-dependent manner. When overexpressed in the mouse, it causes a progeroid phenotype that includes premature cognitive decline, synaptic defects, and hyperphosphorylation of ... |
|
|
Bee venom ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory loss by preventing NF-kappaB pathway.
J. Neuroinflammation 12 , 124, (2015) Accumulation of beta-amyloid and neuroinflammation trigger Alzheimer's disease. We previously found that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) caused neuroinflammation with concomitant accumulation of beta-amyloid peptides leading to memory loss. A variety of anti-inflamm... |
|
|
Neurotoxocarosis alters myelin protein gene transcription and expression.
Parasitol. Res. 114 , 2175-86, (2015) Neurotoxocarosis is an infection of the central nervous system caused by migrating larvae of the common dog and cat roundworms (Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati), which are zoonotic agents. As these parasites are prevalent worldwide and neuropathological and ... |
|
|
Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 knockout reduces cognitive impairment and pathogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Mol. Brain 7 , 40, (2014) Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology occurs in part as the result of excessive production of β-amyloid (Aβ). Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) is now considered a receptor for Aβ and consequently contributes to pathogenic Aβ signaling in AD.Genetic del... |
|
|
Altered amyloid precursor protein processing regulates glucose uptake and oxidation in cultured rodent myotubes.
Diabetologia 57(8) , 1684-92, (2014) Impaired glucose uptake in skeletal muscle is an important contributor to glucose intolerance in type 2 diabetes. The aspartate protease, beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), a critical regulator of amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing, modulates in... |