4-Chlorobenzoic acid
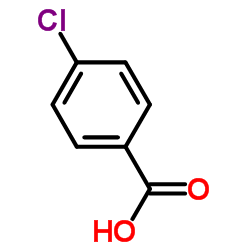
4-Chlorobenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 4-Chlorobenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 74-11-3 | Molecular Weight | 156.566 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 287.2±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO2 | Melting Point | 238-241 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 127.5±19.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Kinetics of the esterification of active pharmaceutical ingredients containing carboxylic acid functionality in polyethylene glycol: formulation implications.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(8) , 2424-33, (2014) Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are attractive as excipients in the manufacture of drug products because they are water soluble and poorly immunogenic. They are used in various pharmaceutical preparations. However, because of their terminal hydroxyl groups, PEGs ... |
|
|
Enhanced hydroxyl radical generation in the combined ozonation and electrolysis process using carbon nanotubes containing gas diffusion cathode.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 , 15812-20, (2015) Combination of ozone together with electrolysis (ozone-electrolysis) is a promising wastewater treatment technology. This work investigated the potential use of carbon nanotube (CNT)-based gas diffusion cathode (GDC) for ozone-electrolysis process employing h... |
|
|
Benzenepolycarboxylic acids with potential anti-hemorrhagic properties and structure–activity relationships
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 7000-2, (2011) Previously, we reported the structural requirements of the cinnamic acid relatives for inhibition of snake venom hemorrhagic action. In the present study, we examined the effect of benzenepolycarboxylic acids and substituted benzoic acids against Protobothrop... |
|
|
Investigation of the catalytic mechanism of the hotdog-fold enzyme superfamily Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase.
Biochemistry 51(3) , 786-94, (2012) The 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA (4-HB-CoA) thioesterase from Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS3 catalyzes the final step of the 4-chlorobenzoate degradation pathway, which is the hydrolysis of 4-HB-CoA to coenzyme A (CoA) and 4-hydroxybenzoate (4-HB). In previous work, X-r... |
|
|
Determination of co-metabolism for 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) degradation with enzymes fromTrametes versicolorU97
J. Biosci. Bioeng. , (2012) Trametes versicolor U97 isolated from nature degraded 73% of the 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) in a malt extract liquid medium after a 40-d incubation period. This paper presents a kinetic study of microbial growth using the Monod equat... |
|
|
Cloning of the Arthrobacter sp. FG1 dehalogenase genes and construction of hybrid pathways in Pseudomonas putida strains.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 75(5) , 1111-8, (2007) An Arthrobacter strain, able to utilize 4-chlorobenzoic acid as the sole carbon and energy source, was isolated and characterized. The first step of the catabolic pathway was found to proceed via a hydrolytic dehalogenation that leads to the formation of 4-hy... |
|
|
ImprimatinC1, a novel plant immune-priming compound, functions as a partial agonist of salicylic acid.
Sci. Rep. 2 , 705, (2012) Plant activators are agrochemicals that protect crops from pathogens. They confer durable resistance to a broad range of diseases by activating intrinsic immune mechanisms in plants. To obtain leads regarding useful compounds, we have screened a chemical libr... |
|
|
Production of sulfate radical and hydroxyl radical by reaction of ozone with peroxymonosulfate: a novel advanced oxidation process.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 , 7330-9, (2015) In this work, simultaneous generation of hydroxyl radical (•OH) and sulfate radical (SO4•−) by the reaction of ozone (O3) with peroxymonosulfate (PMS; HSO5−) has been proposed and experimentally verified. We demonstrate that the reaction between the anion of ... |
|
|
[4-chlorobiphenyl and 4-chlorobenzoic acid biodegradation by Rhodococcus ruber P25].
Mikrobiologiia 81(2) , 159-70, (2012)
|
|
|
Photoreactivity of carboxylated single-walled carbon nanotubes in sunlight: reactive oxygen species production in water.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(17) , 6674-9, (2010) Very limited information exists on transformation processes of carbon nanotubes in the natural aquatic environment. Because the conjugated pi-bond structure of these materials is efficient in absorbing sunlight, photochemical transformations are a potential f... |