Chloramphenicol palmitate
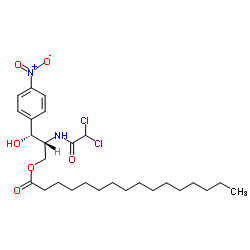
Chloramphenicol palmitate structure
|
Common Name | Chloramphenicol palmitate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 530-43-8 | Molecular Weight | 561.538 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 691.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H42Cl2N2O6 | Melting Point | 90ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 372.1±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Structural, electronic, thermodynamical and charge transfer properties of Chloramphenicol Palmitate using vibrational spectroscopy and DFT calculations.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 101 , 335-42, (2013) The global problem of advancing bacterial resistance to newer drugs has led to renewed interest in the use of Chloramphenicol Palmitate (C27H42Cl2N2O6) [Palmitic acid alpha ester with D-threo-(-),2-dichloro-N-(beta-hydroxy-alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-p-nitropheneth... |
|
|
Metabolism of some drugs by intestinal lactobacilli and their toxicological considerations.
Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 58(1) , 11-5, (1986) The bacterial metabolism of three drugs (sulphasalazine, phthalylsulphathiazole and chloramphenicol palmitate) and two dyes (tartrazine and methyl red) has been studied using a resting culture technique. The strains used were isolated intestinal lactobacilli,... |
|
|
The effect of exocrine pancreatic function on chloramphenicol pharmacokinetics in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Pediatr. Res. 23(4) , 388-92, (1988) The effect of exocrine pancreatic function on the pharmacokinetics of the choramphenicol oral capsule (CAP-base), chloramphenicol palmitate oral liquid (CAP-P), and chloramphenicol succinate intravenous (CAP-S) formulations was evaluated in 10 patients, aged ... |
|
|
Comparative bioavailability of intravenous and oral chloramphenicol in adults.
J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24(4) , 181-6, (1984) The comparative bioavailability of chloramphenicol from intravenous succinate, oral palmitate, and oral base preparations was studied in a crossover manner in 12 adult patients. Chloramphenicol was administered at a dose of 1 Gm every 6 hours, and blood sampl... |
|
|
Arthroderma benhamiae infection in a rabbit.
J. Vet. Med. Sci. 63(8) , 929-31, (2001) The isolate from the rabbit with dermatophytosis which was transmitted to the owners was proved to be Arthroderma benhamiae (-) by mating experiments as well as by chitin synthase 1 (CHSI) gene analysis. |
|
|
Surface area and crystallinity of Form A of chloramphenicol palmitic and stearic esters: which one is the limiting factor in the enzymatic hydrolysis?
J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 39(12) , 1041-3, (1987) Chloramphenicol stearic and palmitic esters in the polymorphic Form A, when ground for 85 h showed an in-vitro enzymatic hydrolysis rate constant (Khydr), the value of which was the same as that of a commercial Form B. The increase in the rate of the enzymati... |
|
|
Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol palmitate in malnourished children.
Indian J. Med. Res. 74 , 244-50, (1981)
|
|
|
Effect of a change in crystal polymorph on the degree of adhesion between micronized drug particles and large homogenous carrier particles during an interactive mixing process.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 9(4) , 387-98, (2004) This study reports the effect of a change in crystal form on the quality of interactive mixtures prepared with homogenous sugar beads and the three polymorphs of chloramphenicol palmitate (CAP). Six mixtures containing micronized CAP polymorph powder (0.5%) a... |
|
|
[Chloramphenicol at a veal-calf stock farm].
Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 111(10) , 471-5, (1986) Chloramphenicol is used in the treatment of respiratory infections in veal calves. Antibiotic resistance of Pasteurella to chloramphenicol was rarely observed upto 1984. The increase was recorded from 1984. The following dosages are recommended on the basis o... |
|
|
[Pseudomorphism of chloramphenicol stearate and palmitate in relationship availability].
Il Farmaco 38(4) , 173-82, (1983)
|