Auraptene
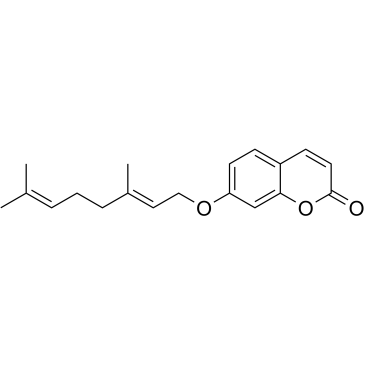
Auraptene structure
|
Common Name | Auraptene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 495-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 298.376 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 455.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 | Melting Point | 66 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 195.4±23.3 °C | |
|
Suppression of mitochondrial respiration with auraptene inhibits the progression of renal cell carcinoma: involvement of HIF-1α degradation.
Oncotarget 6 , 38127-38, (2015) Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) progression resulting from the uncontrolled migration and enhanced angiogenesis is an obstacle to effective therapeutic intervention. Tumor metabolism has distinctive feature called Warburg effect, which enhances the aerobic glycoly... |
|
|
Novel prodrugs for the treatment of colonic diseases based on 5-aminosalicylic acid, 4'-geranyloxyferulic acid, and auraptene: biological activities and analytical assays.
Curr. Drug Deliv. 9(2) , 112-21, (2012) A pro-drug is a substance administered in a pharmacologically inactive structure that, once administered, is metabolised in vivo into the corresponding active principle. The rationale for the design of prodrugs is the optimisation of absorption, distribution,... |
|
|
Development of a quantitative bioassay to assess preventive compounds against inflammation-based carcinogenesis.
Nitric Oxide 25(2) , 183-94, (2011) Reducing cancer incidence and mortality by use of cancer-chemopreventive agents is an important goal. We have established an in vitro bioassay that is able to screen large numbers of candidate chemicals that are positive for prevention of inflammation-related... |
|
|
A natural propenoic acid derivative activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta).
Life Sci. 86(13-14) , 493-8, (2010) Previous studies showed that natural prenyloxyphenylpropanoid derivatives have potent biological properties in vivo. Given the structural similarities between these compounds and known peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists, the present st... |
|
|
Identification, synthesis and quantification of process-related impurities in auraptene.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 56(2) , 191-9, (2011) Impurities in chemically synthesized auraptene, an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), were detected by a gradient reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method. Molecular weights and major product ions of these chemical compounds ... |
|
|
Methyl galbanate, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells.
J. Nat. Med. 65(2) , 353-9, (2011) It is well known that inflammation is associated with various neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. An inflammatory mediator, nitric oxide (NO), is produced by inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in microglia and seems to b... |
|
|
Effects of ATRA combined with citrus and ginger-derived compounds in human SCC xenografts.
BMC Cancer 10 , 394, (2010) NF-kappaB is a survival signaling transcription factor complex involved in the malignant phenotype of many cancers, including squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). The citrus coumarin, auraptene (AUR), and the ethno-medicinal ginger (Alpinia galanga) phenylpropanoi... |
|
|
Auraptene and its effects on the re-emergence of colon cancer stem cells.
Phytother Res. 27(5) , 784-6, (2013) Recent studies indicate that auraptene (7-geranyloxycoumarin, AUR), a geranyloxycoumarin extracted from fruits of edible plants belonging to the Rutaceae family, may represent a novel lead compound for dietary colon cancer chemoprevention in rodents. As a con... |
|
|
Citrus auraptene: a potential multifunctional therapeutic agent for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Ann. Hepatol. 10(4) , 575-7, (2011)
|
|
|
Potential benefits of supplementation with auraptene in cystic fibrosis.
Clin. Nutr. 30(2) , 259-60, (2011)
|