495-02-3
| Name | auraptene |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
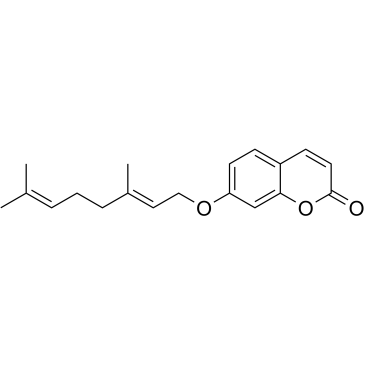
Auraptene
7-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromen-2-one 7-[[(2E)-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-yl]oxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one 7-Geranyloxycoumarin Aurapten 7-{[(2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromen-2-one 7-Geranyloxycoumarin 7-{[(2E)-3,7-Diméthyl-2,6-octadièn-1-yl]oxy}-2H-chromén-2-one aurapten |
| Description | Auraptene is the most abundant naturally occurring geranyloxycoumarin. Auraptene is primarily isolated from plants in the Rutaceae family, such as citrus fruits. Auraptene decreases the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) as well as key inflammatory mediators, including IL-6, IL-8, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand-5(CCL5)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
MMP-2 |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 455.5±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 66 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 298.376 |
| Flash Point | 195.4±23.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 298.156891 |
| PSA | 39.44000 |
| LogP | 5.69 |
| Appearance | white to off-white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.549 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
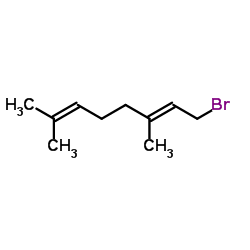
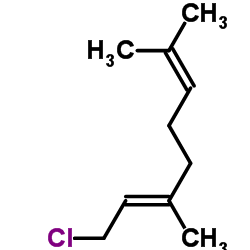
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
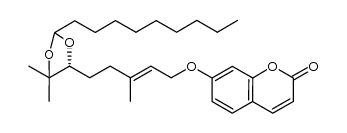
| DownStream 5 | |



![2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one,7-[[(2E)-3-(4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-furanyl)-2-buten-1-yl]oxy] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/234/36413-91-9.png)
![7-[(E)-3-(5,5-dimethyl-4-oxooxolan-2-yl)but-2-enoxy]chromen-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/98066-12-7.png)
![Coumarin, 7-[ (6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenyl)oxy] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/231/5980-09-6.png)
