3-氨基甲酰-1-甲基氯化吡啶
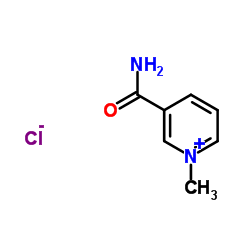
3-氨基甲酰-1-甲基氯化吡啶结构式

|
常用名 | 3-氨基甲酰-1-甲基氯化吡啶 | 英文名 | nicotinamide chloromethylate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 1005-24-9 | 分子量 | 172.612 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C7H9ClN2O | 熔点 | 207-209℃ (water acetone ) | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
¹H nuclear magnetic resonance based metabolic urinary profiling of patients with ischemic heart failure.
Clin. Biochem. 44(4) , 293-9, (2011) We sought to identify metabolic pathways characterizing human heart failure (HF) using ¹NMR based urinary metabolomic analysis in conjunction with multivariate statistics.Patients with systolic HF of ischemic origin (n=15) and healthy controls (n=20) particip... |
|
|
Nicotinamide supplementation induces detrimental metabolic and epigenetic changes in developing rats.
Br. J. Nutr. 110(12) , 2156-64, (2013) Ecological evidence suggests that niacin (nicotinamide and nicotinic acid) fortification may be involved in the increased prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes, both of which are associated with insulin resistance and epigenetic changes. The purpose of th... |
|
|
Single bout of endurance exercise increases NNMT activity in the liver and MNA concentration in plasma; the role of IL-6.
Pharmacol. Rep. 64(2) , 369-76, (2012) Methylnicotinamide (MNA) displays vasoprotective activity, however, the regulation of the activity of nicotinamide-N-methyltransferase (NNMT), is largely unknown. We analyze a possible involvement of IL-6 in the activation of NNMT-MNA pathway during an endura... |
|
|
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) and 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA) in experimental hepatitis induced by concanavalin A in the mouse.
Pharmacol. Rep. 62(3) , 483-93, (2010) Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), which converts nicotinamide (NA) to 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA), is up-regulated in the cirrhotic liver. Because MNA displays PGI(2)-dependent anti-inflammatory effects, the up-regulation of NNMT may play a regulatory r... |
|
|
Excessive nicotinic acid increases methyl consumption and hydrogen peroxide generation in rats.
Pharm. Biol. 51(1) , 8-12, (2013) Recent ecological evidence has showed a lag-correlation between the prevalence of diabetes and consumption of niacin (nicotinamide and nicotinic acid) in the US. Nicotinamide has been demonstrated to induce insulin resistance due to excess reactive oxygen spe... |
|
|
1-methylnicotinamide effects on the selected markers of endothelial function, inflammation and haemostasis in diabetic rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 640(1-3) , 157-62, (2010) 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA) is a primary metabolite of nicotinamide. In recent years several activities of MNA have been described, such as anti-inflammatory activity in skin diseases, induction of prostacyclin synthesis via COX-2, aortal endothelium protectio... |
|
|
Effect of selected NAD+ analogues on mitochondria activity and proliferation of endothelial EA.hy926 cells.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 640(1-3) , 102-11, (2010) The aim of the study was to examine the effect of 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA) and 1-methyl-3-nitropyridine (MNP) on mitochondria activity and proliferation of endothelial EA.hy926 cells. The activity of MNA was also referred to nicotinamide (NAM) being MNA met... |
|
|
N-Methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide is 1-methylnicotinamide metabolite of low cyclooxygenase-dependent vasodilating activity.
J. Physiol. Biochem. 68(3) , 329-34, (2012) 1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA) is a primary metabolite of nicotinamide recently proven to cause systemic increase in PGI(2) plasma levels in an unknown mechanism. Our present study was aimed at verifying whether the increased production of PGI(2), a vasodilating ... |
|
|
1-methylnicotinamide (MNA) in prevention of diabetes-associated brain disorders.
Neurochem. Int. 56(2) , 221-8, (2010) The present study has been designed to establish the potential benefits from 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA) treatment on brain disorders associated with type 1 diabetes. All experiments were carried out after 6 weeks of streptozotocin-induced diabetes (60 mg/kg o... |
|
|
Decreased skin-mediated detoxification contributes to oxidative stress and insulin resistance.
Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012 , 128694, (2012) The skin, the body's largest organ, plays an important role in the biotransformation/detoxification and elimination of xenobiotics and endogenous toxic substances, but its role in oxidative stress and insulin resistance is unclear. We investigated the relatio... |