(4S,5R)-4-羟基-5-(羟甲基)二氢呋喃-2(3H)-酮
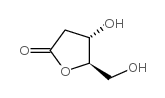
(4S,5R)-4-羟基-5-(羟甲基)二氢呋喃-2(3H)-酮结构式

|
常用名 | (4S,5R)-4-羟基-5-(羟甲基)二氢呋喃-2(3H)-酮 | 英文名 | (4S,5R)-4-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 34371-14-7 | 分子量 | 132.11500 | |
| 密度 | 1.438g/cm3 | 沸点 | 395.3ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C5H8O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 179.1ºC |
|
Reduced repair capacity of a DNA clustered damage site comprised of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine and 2-deoxyribonolactone results in an increased mutagenic potential of these lesions.
Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 762 , 32-9, (2014) A signature of ionizing radiation is the induction of DNA clustered damaged sites. Non-double strand break (DSB) clustered damage has been shown to compromise the base excision repair pathway, extending the lifetimes of the lesions within the cluster, compare... |
|
|
Analysis of base excision DNA repair of the oxidative lesion 2-deoxyribonolactone and the formation of DNA-protein cross-links.
Meth. Enzymol. 408 , 48-64, (2006) DNA base lesions arising from oxidation or alkylation are processed primarily by the base excision repair pathway (BER). The damaged bases are excised by DNA N-glycosylases, which generate apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites; AP sites produced by hydrolytic deca... |
|
|
Histone-catalyzed cleavage of nucleosomal DNA containing 2-deoxyribonolactone.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(19) , 8090-3, (2012) Oxidized abasic sites such as 2-deoxyribonolactone (L) are produced in DNA by a variety of oxidizing agents, including potent cytotoxic antitumor natural products. 2-Deoxyribonolactone is labile under alkaline conditions, but its half-life in free DNA at pH 7... |
|
|
Mutagenic effects of abasic and oxidized abasic lesions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Nucleic Acids Res. 33(19) , 6196-202, (2005) 2-deoxyribonolactone (L) and 2-deoxyribose (AP) are abasic sites that are produced by ionizing radiation, reactive oxygen species and a variety of DNA damaging agents. The biological processing of the AP site has been examined in the yeast Saccharomyces cerev... |
|
|
Use of fluorescence sensors to determine that 2-deoxyribonolactone is the major alkali-labile deoxyribose lesion produced in oxidatively damaged DNA.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46(4) , 561-4, (2007)
|
|
|
2-Deoxyribonolactone lesions in X-ray-irradiated DNA: quantitative determination by catalytic 5-methylene-2-furanone release.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44(38) , 6210-3, (2005)
|
|
|
Synthesis and analysis of oligonucleotides containing abasic site analogues.
J. Org. Chem. 73(7) , 2695-703, (2008) DNA damage results in the formation of abasic sites from the formal hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond (AP) and several oxidized abasic lesions. Previous studies on AP sites revealed that DNA polymerases preferentially incorporated dA opposite them in approxim... |
|
|
Photogeneration of 2-deoxyribonolactone in benzophenone-purine dyads. Formation of ketyl-C1' biradicals.
Org. Lett. 10(20) , 4409-12, (2008) Photolysis of the title dyads under aerobic conditions leads to a 2-deoxyribonolactone derivative. Laser flash photolysis reveals that the process occurs from the short-lived benzophenone-like triplet excited state. A mechanism involving intramolecular electr... |
|
|
Hydrogen bonding contributes to the selectivity of nucleotide incorporation opposite an oxidized abasic lesion.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(19) , 6080-1, (2008) The ability of DNA polymerases to maintain the integrity of the genome even after it has been structurally altered is vital. There is considerable interest in determining the structural properties of the DNA template that polymerases recognize when determinin... |
|
|
Diastereocontrolled electrophilic fluorinations of 2-deoxyribonolactone: syntheses of all corresponding 2-deoxy-2-fluorolactones and 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-NAD+s.
J. Org. Chem. 74(16) , 5779-89, (2009) Methods to construct 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro nucleosides have undergone limited improvement in the last 20 years in spite of the substantially increased value of these compounds as pharmaceuticals and as tools for studying biological processes. We herein describe ... |