1,3-二甲基尿嘧啶
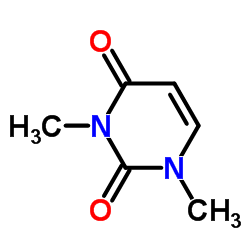
1,3-二甲基尿嘧啶结构式

|
常用名 | 1,3-二甲基尿嘧啶 | 英文名 | 1,3-Dimethyluracil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 874-14-6 | 分子量 | 140.140 | |
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 208.4±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H8N2O2 | 熔点 | 119-122 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 84.3±15.0 °C |
|
Excited state structures and decay dynamics of 1,3-dimethyluracils in solutions: resonance Raman and quantum mechanical calculation study.
J. Phys. Chem. B 117(39) , 11660-9, (2013) The resonance Raman spectroscopic study of the excited state structural dynamics of 1,3-dimethyluracil (DMU), 5-bromo-1,3-dimethyluracil (5BrDMU), uracil, and thymine in water and acetonitrile were reported. Density functional theory calculations were carried... |
|
|
Ionization of dimethyluracil dimers leads to facile proton transfer in the absence of hydrogen bonds.
Nature Chemistry 4(4) , 323-9, (2012) Proton transfer is ubiquitous in chemistry and biology, occurring, for example, in proteins, enzyme reactions and across proton channels and pumps. However, it has always been described in the context of hydrogen-bonding networks ('proton wires') acting as pr... |
|
|
The SO4(.-)-induced chain reaction of 1,3-dimethyluracil with peroxodisulphate.
Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 51(3) , 441-53, (1987) The sulphate radical SO4(.-) reacts with 1,3-dimethyluracil (1,3-DMU) (k = 5 X 10(9) dm3 mol-1 s-1) thereby forming with greater than or equal to 90 per cent yield the 1,3-DMU C(5)-OH adduct radical 4 as evidenced by its absorption spectrum and its reactivity... |
|
|
Equilibrium of formation of the 6-carbanion of UMP, a potential intermediate in the action of OMP decarboxylase.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(47) , 13986-7, (2002) There has been some speculation that the C-6 position in UMP may be unusually acidic, stabilizing a carbanion that is generated at this position during OMP decarboxylation. On the basis of the rate of OH- catalyzed deuterium exchange at elevated temperatures ... |
|
|
Probing noncovalent interactions in biomolecular crystals with terahertz spectroscopy.
ChemPhysChem 9(4) , 544-7, (2008)
|
|
|
Synthesis of pyrazolo[1,5-alpha]pyrimidinone regioisomers.
J. Org. Chem. 72(3) , 1043-6, (2007) This work describes two distinct routes to prepare pyrazolo[1,5-alpha]pyrimidin-7-ones and two distinct routes to prepare pyrazolo[1,5-alpha]pyrimidin-5-ones. Use of 1,3-dimethyluracil as the electrophile in the preparation of the pyrimidin-5-one regioisomer ... |
|
|
Fenton chemistry of 1,3-dimethyluracil.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(37) , 9007-14, (2001) Hydroxyl radicals were generated in the Fenton reaction at pH 4 (Fe(2+) + H(2)O(2) --> Fe(3+) + .OH + OH-, k approximately equal to 60 L mol(-1) s(-1)) and by pulse radiolysis (for the determination of kinetic data). They react rapidly with 1,3-dimethyluracil... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of 16 purine derivatives in urinary calculi by gradient reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 819(2) , 229-35, (2005) A reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method with ultraviolet detection has been developed for the analysis of purines in urinary calculi. The method using gradient of methanol concentration and pH was able to separate 16 compounds: u... |
|
|
Zooming into pi-stacked manifolds of nucleobases: ionized states of dimethylated uracil dimers.
J. Phys. Chem. A 114(4) , 2001-9, (2010) The electronic structure of 1,3-dimethyluracil and its dimer is characterized by ab initio calculations. The methylation eliminates the H-bonded isomers and allows one to focus on the pi-stacked manifold. In the neutral species, methylation increases the bind... |
|
|
Uracil and thymine reactivity in the gas phase: the S(N)2 reaction and implications for electron delocalization in leaving groups.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 , 18376-18385, (2009) The gas-phase substitution reactions of methyl chloride and 1,3-dimethyluracil (at the N1-CH(3)) are examined computationally and experimentally. It is found that, although hydrochloric acid and 3-methyluracil are similar in acidity, the leaving group abiliti... |