双(1,3-二乙基硫代巴比妥酸)三次甲基氧杂菁
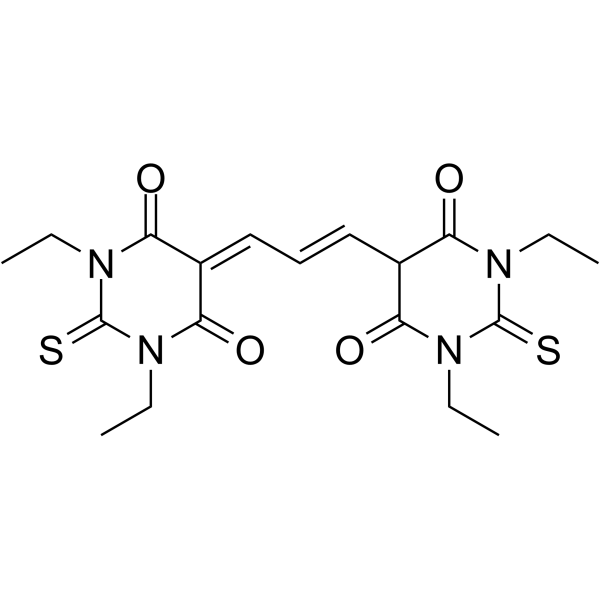
双(1,3-二乙基硫代巴比妥酸)三次甲基氧杂菁结构式

|
常用名 | 双(1,3-二乙基硫代巴比妥酸)三次甲基氧杂菁 | 英文名 | Bis-(1,3-diethylthiobarbituric acid)trimethine oxonol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 47623-98-3 | 分子量 | 436.54800 | |
| 密度 | 1.42g/cm3 | 沸点 | 464.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C19H24N4O4S2 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 234.8ºC |
|
Membrane potential changes visualized in complete growth media through confocal laser scanning microscopy of bis-oxonol-loaded cells.
Exp. Cell Res. 231(2) , 260-8, (1997) Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) was employed to visualize and measure membrane potential changes in several types of cultured adherent cells, such as human fibroblasts, mouse mammary tumor C127 cells, and human saphenous vein endothelial cells, prel... |
|
|
Peroxynitrite affects Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent calcium channels.
J. Neurochem. 76(2) , 341-50, (2001) The effect of peroxynitrite (OONO-) on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (VDCCs) was examined by measuring [45Ca2+] influx into mouse cerebral cortical neurones. OONO- time- and dose-dependently increased [45Ca2+] influx and this increase was abolished by manga... |
|
|
Simultaneous mechanical stiffness and electrical potential measurements of living vascular endothelial cells using combined atomic force and epifluorescence microscopy.
Nanotechnology 20(17) , 175104, (2009) The degree of mechanical stiffness of vascular endothelial cells determines the endogenous production of the vasodilating gas nitric oxide (NO). However, the underlying mechanisms are not yet understood. Experiments on vascular endothelial cells suggest that ... |
|
|
A membrane potential-sensitive dye for vascular smooth muscle cells assays.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301(1) , 113-8, (2003) Changes in membrane potential of rat aorta smooth muscle cells were investigated using the bis-oxonol sensitive probe DIBAC2(3). We compared the changes in membrane potential induced by a high external KCl concentration in aorta smooth muscle cells from normo... |
|
|
Measurement of membrane potential of endothelial cells in single perfused microvessels.
Microvasc. Res. 50(2) , 183-98, (1995) The membrane potential is an important modulator of calcium ion flux into endothelial cells of venular microvessels. We developed a method to measure the membrane potential of endothelial cells forming the walls of individually perfused microvessels under the... |
|
|
Discrimination between cystic fibrosis and CFTR-corrected epithelial cells by a membrane potential-sensitive probe.
Exp. Lung Res. 28(3) , 181-99, (2002) Methods to detect functional cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) are needed for the assessment of new therapies in cystic fibrosis (CF). We have combined patch-clamp and fluorimetric techniques to investigate whether the fluorescent vol... |
|
|
Effect of acute hypoxia on glomus cell Em and psi m as measured by fluorescence imaging.
J. Appl. Physiol. 93(6) , 1987-98, (2002) We have reinvestigated the hypothesis of the relative importance of glomus cell plasma and mitochondrial membrane potentials (E(m) and psi(m), respectively) in acute hypoxia by a noninvasive fluorescence microimaging technique using the voltage-sensitive dyes... |
|
|
Cyclic AMP-induced depolarization measured by bis-oxonol fluorescence in bovine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells.
J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 97(1) , 65-72, (1994) Effects of cyclic AMP on membrane potentials were examined by measuring the changes of bis-oxonol fluorescence in bovine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. 8-Bromo cyclic AMP (8Br-cAMP) or forskolin caused a gradual and long lasting increase of the fluoresce... |
|
|
Mapping of capillary flow, cellular redox state, and resting membrane potential in hypoperfused rat myocardium.
Am. J. Physiol. 277(5 Pt 2) , H2050-64, (1999) The influence on myocyte viability of ischemia-induced changes in capillary perfusion was studied in the hearts of anesthetized rats subjected to partial occlusion of the left coronary artery for 45 min. Timed plasma labeling was applied to determine perfusio... |
|
|
Involvement of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in the response of membrane potential to hyperosmolality in cultured human aorta endothelial cells.
Anesth. Analg. 100(2) , 419-26, (2005) The membrane potential of endothelial cells is an important determinant of endothelial functions, including regulation of vascular tone. We investigated whether adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels were involved in the response of memb... |