阿伐麦布
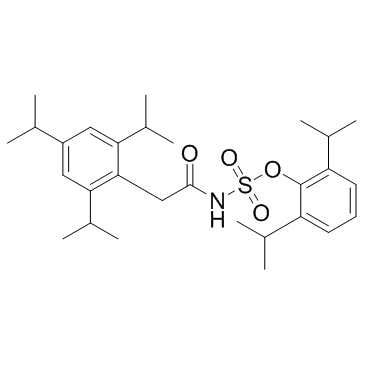
阿伐麦布结构式

|
常用名 | 阿伐麦布 | 英文名 | Avasimibe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 166518-60-1 | 分子量 | 501.721 | |
| 密度 | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C29H43NO4S | 熔点 | 178-180° (Lee); mp 169.5-170.4° (Dozeman) | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
Statin therapy alone and in combination with an acyl-CoA:cholesterol O-acyltransferase inhibitor on experimental atherosclerosis.
Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 36(1) , 9-17, (2007) The ability to modify the enzymatic processes involved in promoting atherosclerotic plaque disruption and to serially monitor atherosclerotic evolution could provide novel information in the management of patients with atherosclerosis. We studied the effects ... |
|
|
Coronary circulatory function in patients with the metabolic syndrome.
J. Nucl. Med. 52(9) , 1369-77, (2011) The metabolic syndrome affects 25% of the U.S. population and greatly increases the risk of diabetes and coronary artery disease (CAD). We tested the hypothesis that the metabolic syndrome is associated with impaired coronary vasodilator function, a marker of... |
|
|
Avasimibe and atorvastatin synergistically reduce cholesteryl ester content in THP-1 macrophages.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 451(1) , 11-7, (2002) Evidence suggests that the inhibition of both acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase and hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA reductase causes a synergistic direct antiatherosclerotic effect on the vessel wall. To investigate this synergism in a single cell type and to a... |
|
|
Anti-atherogenic effects of the acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor, avasimibe (CI-1011), in cultured primary human macrophages.
Atherosclerosis 161(1) , 45-54, (2002) Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitors have been shown to reduce atherosclerotic lesions in animals; however, the mechanism(s) for this effect remains unclear. Therefore, we used cultured primary human monocyte-derived macrophages (HMMs) to ex... |
|
|
Effects of avasimibe on cytochrome P450 2C9 expression in vitro and in vivo.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 32(12) , 1370-6, (2004) Avasimibe, an acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor, has been previously shown to be a potent inducer of CYP3A4 and multiple drug resistance protein 1. We have further characterized the drug interaction potential of avasimibe by studying the inductiv... |
|
|
New advances in lipid-modifying therapies for reducing cardiovascular risk.
Cardiology 97(2) , 59-66, (2002) Over the last 30 years, several epidemiological and prospective studies have identified a number of risk factors for the development of cardiovascular disease. Lipid abnormalities are central among these risk factors, and their correction has been a major tar... |
|
|
Cardiovascular drugs inhibit MMP-9 activity from human THP-1 macrophages.
DNA Cell. Biol. 23(5) , 283-92, (2004) It is now recognized that atherosclerosis complications are related to the unstable character of the plaque rather than its volume. Vulnerable plaques often contain a large lipid core, a reduced content of smooth muscle cells, and accumulation of inflammatory... |
|
|
The effect of inhibition of acyl coenzyme A-cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) on exercise performance in patients with peripheral arterial disease.
Vasc. Med. 9(4) , 271-7, (2004) This study tested the hypothesis that avasimibe, an inhibitor of acyl coenzyme A-cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT), would improve treadmill exercise performance in patients with claudication secondary to peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Four hundred and fo... |
|
|
Effects of the acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor avasimibe on human atherosclerotic lesions.
Circulation 110(21) , 3372-7, (2004) Inhibition of the acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) enzyme may prevent excess accumulation of cholesteryl esters in macrophages. The ACAT inhibitor avasimibe was shown to reduce experimental atherosclerosis. This study was designed to investi... |
|
|
Comparison of intravascular ultrasound and quantitative coronary angiography for the assessment of coronary artery disease progression.
Circulation 115(14) , 1851-7, (2007) The relative merits of quantitative coronary analysis (QCA) and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) for the assessment of progression/regression in coronary artery disease are uncertain. To explore this subject further, we analyzed the angiographic and IVUS data ... |