1-辛酸甘油单酯
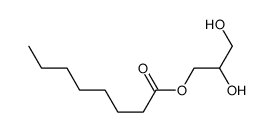
1-辛酸甘油单酯结构式

|
常用名 | 1-辛酸甘油单酯 | 英文名 | Monoctanoin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 502-54-5 | 分子量 | 218.29000 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C11H22O4 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
How relevant are assembled equilibrium samples in understanding structure formation during lipid digestion?
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 96 , 117-24, (2015) Lipid-based formulations are gaining interest for use as drug delivery systems for poorly water-soluble drug compounds. During digestion, the lipolysis products self-assemble with endogenous surfactants in the gastrointestinal tract to form colloidal structur... |
|
|
Transcutaneous delivery of leflunomide nanoemulgel: Mechanistic investigation into physicomechanical characteristics, in vitro anti-psoriatic and anti-melanoma activity.
Int. J. Pharm. 487 , 148-56, (2015) The present study is a mechanistic validation of 'proof of concept' of effective topical delivery of leflunomide (LFD) nanoemulgel for localized efficient treatment of psoriatic lesions as well as melanoma affected skin regions. Hyperproliferation of keratino... |
|
|
Solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) of darunavir for improved dissolution and oral bioavailability: In vitro and in vivo evaluation.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 74 , 1-10, (2015) The current study was aimed to investigate the potential of solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (S-SNEDDS) composed of Capmul MCM C8 (oil), Tween 80 (surfactant) and Transcutol P (co-surfactant) in improving the dissolution and oral bioavailabilit... |
|
|
A self-microemulsifying drug delivery system to overcome intestinal resveratrol toxicity and presystemic metabolism.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(11) , 3491-500, (2014) A mixed lipid-mixed surfactant self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) was developed to exploit the health benefits of resveratrol, a Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class 2 natural polyphenol, subject to extensive intestinal presystemic m... |
|
|
Development of DH-I-180-3 loaded lipid nanoparticle for photodynamic therapy.
Int. J. Pharm. 491 , 393-401, (2015) Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising noninvasive treatment modality for cancer. Photosensitizer and specific wave length of light are the key component of PDT. DH-I-180-3, a second generation photosensitizer, was incorporated into lipid nanoparticle for ... |
|
|
Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. on alfalfa seeds by caprylic acid and monocaprylin.
Int. J. Food Microbiol. 144 , 141-146, (2010) Alfalfa and other seed sprouts have been implicated in several Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. human illness outbreaks in the U.S. Continuing food safety issues with alfalfa seeds necessitate the need for discovery and use of novel and effective ... |
|
|
Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes on frankfurters by monocaprylin alone or in combination with acetic acid.
J. Food Prot. 70 , 1594-1599, (2007) The antilisterial activity of monocaprylin (MC) and its combination with acetic acid (AA) on frankfurters was investigated. Each frankfurter was surface inoculated with a three-strain mixture of Listeria monocytogenes to obtain an inoculation level of 4.0 log... |
|
|
Susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni to organic acids and monoacylglycerols.
Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 55 , 215-220, (2010) Organic acids can be used as feed supplements or for treatment of poultry carcasses in processing plants. The antimicrobial activity of nineteen organic acids and two monoacylglycerols in cultures of Campylobacter jejuni CCM 6214(T) (ATCC 33560) was determine... |
|
|
In vitro antimicrobial properties of caprylic acid, monocaprylin, and sodium caprylate against Dermatophilus congolensis.
Am. J. Vet. Res. 72 , 331-335, (2011) To determine antimicrobial effects of caprylic acid and its derivatives, monocaprylin and sodium caprylate, on Dermatophilus congolensis and to determine effects of caprylic acid on the ultrastructure of D congolensis by use of transmission electron microscop... |
|
|
Development of isradipine loaded self-nano emulsifying powders for improved oral delivery: in vitro and in vivo evaluation.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41 , 753-63, (2015) Isradipine (ISR) is a potent calcium channel blocker with low oral bioavailability due to low aqueous solubility, extensive first-pass metabolism and P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated efflux transport. In the present investigation, an attempt was made to develop... |