N-(6-氨基己基)-5-氯-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐
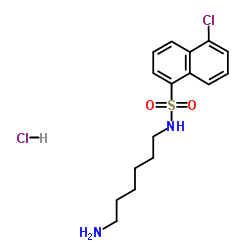
N-(6-氨基己基)-5-氯-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | N-(6-氨基己基)-5-氯-1-萘磺酰胺盐酸盐 | 英文名 | W-7 hydrochloride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 61714-27-0 | 分子量 | 377.329 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 518.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C16H22Cl2N2O2S | 熔点 | 220-222 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 267.6ºC |
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical phenotypes in Plasmodium falciparum.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009) Studies of gene function and molecular mechanisms in Plasmodium falciparum are hampered by difficulties in characterizing and measuring phenotypic differences between individual parasites. We screened seven parasite lines for differences in responses to 1,279... |
|
|
Calmodulin antagonists induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vitro and inhibit tumor growth in vivo in human multiple myeloma.
BMC Cancer 14 , 882, (2014) Human multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable hematological malignancy for which novel therapeutic agents are needed. Calmodulin (CaM) antagonists have been reported to induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor cell invasion and metastasis in various tumor models. How... |
|
|
Calmodulin and PI(3,4,5)P₃ cooperatively bind to the Itk pleckstrin homology domain to promote efficient calcium signaling and IL-17A production.
Sci. Signal. 7(337) , ra74, (2014) Precise regulation of the kinetics and magnitude of Ca(2+) signaling enables this signal to mediate diverse responses, such as cell migration, differentiation, vesicular trafficking, and cell death. We showed that the Ca(2+)-binding protein calmodulin (CaM) a... |
|
|
Social feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans is modulated by antipsychotic drugs and calmodulin and may serve as a protophenotype for asociality.
Neuropharmacology 92 , 56-62, (2015) Here, we define a protophenotype as an endophenotype that has been conserved during evolution. Social feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans may be an example of a protophenotype related to asociality in schizophrenia. It is regulated by the highly conserved neuro... |
|
|
Multidirectional effects of calmodulin kinase II on transmitter release in mature and newly formed mouse motor synapses.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 154(3) , 316-9, (2013) Calmodulin inhibitor W-7 did not cause changes in the quantal content of postsynaptic end-plate potentials (EPP) in newly formed synapses, but prevented facilitation of acetylcholine secretion induced by L-type Ca(2+)channels blocker nitrendipine. CaMKII inhi... |
|
|
Ca2+ signaling regulates ecmB expression, cell differentiation and slug regeneration in Dictyostelium.
Differentiation 84(2) , 163-75, (2012) Ca(2+) regulates cell differentiation and morphogenesis in a diversity of organisms and dysregulation of Ca(2+) signal transduction pathways leads to many cellular pathologies. In Dictyostelium Ca(2+) induces ecmB expression and stalk cell differentiation in ... |
|
|
Calcium-calmodulin signaling elicits mitochondrial dysfunction and the release of cytochrome c during cadmium-induced apoptosis in primary osteoblasts.
Toxicol. Lett. 224(1) , 1-6, (2014) Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal used in industry and is associated with adverse effects on human health following long- or short-term environmental exposure. Although Cd is known to induce apoptosis in many human organ systems, the mechanism that underlie... |
|
|
Interrelationship between calmodulin (CaM) and H2O2 in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defense in the seedlings of Panax ginseng.
Mol. Biol. Rep. 39(7) , 7327-38, (2012) Calmodulin (CaM), the predominant Ca(2+) receptors, is one of the best-characterized Ca(2+) sensors in all eukaryotes. In this study the role of CaM and the possible interrelationship between CaM and hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) in abscisic acid (ABA) induced... |
|
|
Biochemical characterization of a recombinant Swainsona canescens calcium-dependent protein kinase (ScCPK1).
Plant Physiol. Biochem. 54 , 27-33, (2012) Calcium-dependent protein kinases (CPKs) constitute a unique family of kinases involved in many physiological responses in plants. Biochemical and kinetic properties of a recombinant Swainsona canescens calcium-dependent protein kinase (ScCPK1) were examined ... |
|
|
A quantitative analysis to unveil specific binding proteins for bioactive compounds.
Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 26(4) , 249-54, (2013) The mechanisms of the action of bioactive compounds discovered via 'black box' assays using phenotypic indicators generally remain unknown, with the major challenges being the identification of target proteins. In this study, we aimed to develop an efficient ... |