丹磺酰基-L-丙氨酸环己胺盐
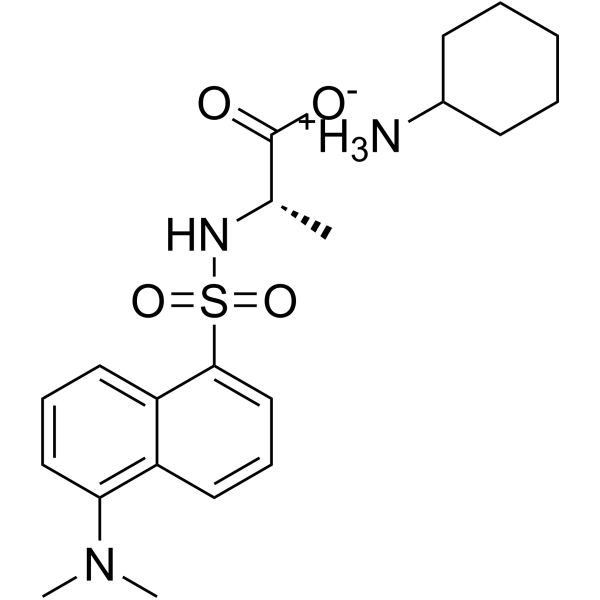
丹磺酰基-L-丙氨酸环己胺盐结构式

|
常用名 | 丹磺酰基-L-丙氨酸环己胺盐 | 英文名 | DANSYL-L-ALANINE CYCLOHEXYLAMMONIUM SALT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 53332-27-7 | 分子量 | 421.55400 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 526ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C21H31N3O4S | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 271.9ºC |
|
A genetically encoded fluorescent amino acid. Summerer, D., et al.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 , 9785-9, (2006)
|
|
|
Genetically encoding unnatural amino acids for cellular and neuronal studies.
Nat. Neurosci. 10 , 1063-72, (2007) Proteins participate in various biological processes and can be harnessed to probe and control biological events selectively and reproducibly, but the genetic code limits the building block to 20 common amino acids for protein manipulation in living cells. Th... |
|
|
A genetically encoded fluorescent amino acid.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 , 9785-9789, (2006) The ability to introduce fluorophores selectively into proteins provides a powerful tool to study protein structure, dynamics, localization, and biomolecular interactions both in vitro and in vivo. Here, we report a strategy for the selective and efficient bi... |
|
|
Expanding the genetic code of yeast for incorporation of diverse unnatural amino acids via a pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132 , 14819-14824, (2010) We report the discovery of a simple system through which variant pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA(CUA Pyl) pairs created in Escherichia coli can be used to expand the genetic code of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In the process we have solved the key challenges of... |
|
|
Genetic incorporation of a small, environmentally sensitive, fluorescent probe into proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 , 12921-12923, (2009) Here, we report that the fluorescent amino acid, 3-(6-acetylnaphthalen-2-ylamino)-2-aminopropanoic acid (Anap), can be genetically incorporated into proteins in yeast with excellent selectivity and efficiency by means of an orthogonal tRNA/aminoacyl-tRNA synt... |
|
|
Esterification of an unnatural amino acid structurally deviating from canonical amino acids promotes its uptake and incorporation into proteins in mammalian cells.
ChemBioChem. 11 , 2268-72, (2010)
|