马加宁I
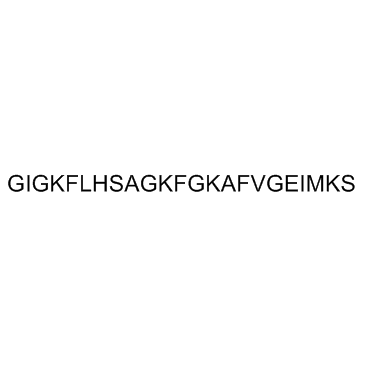
马加宁I结构式

|
常用名 | 马加宁I | 英文名 | Magainin 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 108433-99-4 | 分子量 | 2409.85000 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | N/A | |
| 分子式 | C112H177N29O28S | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | N/A |
|
Targeting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with short salt-resistant synthetic peptides.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(7) , 4113-22, (2014) The seriousness of microbial resistance combined with the lack of new antimicrobials has increased interest in the development of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) as novel therapeutics. In this study, we evaluated the antimicrobial activities of two short synthe... |
|
|
In vitro efficacy of a synthetic all-d antimicrobial peptide against clinically isolated drug-resistant strains.
Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 35(2) , 208-9, (2010)
|
|
|
NMR structural studies of membrane proteins.
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8(5) , 640-8, (1998) The three-dimensional structures of membrane proteins are essential for understanding their functions, interactions and architectures. Their requirement for lipids has hampered structure determination by conventional approaches. With optimized samples, it is ... |
|
|
Electrical detection of pathogenic bacteria via immobilized antimicrobial peptides.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107(45) , 19207-12, (2010) The development of a robust and portable biosensor for the detection of pathogenic bacteria could impact areas ranging from water-quality monitoring to testing of pharmaceutical products for bacterial contamination. Of particular interest are detectors that c... |
|
|
The antibacterial activity of Magainin I immobilized onto mixed thiols Self-Assembled Monolayers.
Biomaterials 30(21) , 3503-12, (2009) An antibacterial peptide, Magainin I, was covalently bound to a mixed 11-mercaptoundecanoïc acid (MUA) and 6-mercaptohexanol (C6OH) (ratio 1:3) Self-Assembled Monolayer (SAM) on gold surfaces. Each step of the surface functionalization was characterized by Po... |
|
|
Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by alpha-helical antimicrobial and cell non-selective membrane-lytic peptides.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1462 , 55-70 , (1999) Permeation of the cell membrane leading to cell death is a mechanism used by a large number of membrane-lytic peptides. Some are linear, mostly helical, and others contain one or more disulfide bonds forming beta-sheet or both beta-sheet and alpha-helix struc... |
|
|
The structure, dynamics and orientation of antimicrobial peptides in membranes by multidimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1462(1-2) , 157-83, (1999) Linear peptide antibiotics have been isolated from amphibians, insects and humans and used as templates to design cheaper and more potent analogues for medical applications. Peptides such as cecropins or magainins are < or = 40 amino acids in length. Many of ... |
|
|
Characterization of unique amphipathic antimicrobial peptides from venom of the scorpion Pandinus imperator.
Biochem. J. 359(Pt 1) , 35-45, (2001) Two novel antimicrobial peptides have been identified and characterized from venom of the African scorpion Pandinus imperator. The peptides, designated pandinin 1 and 2, are alpha-helical polycationic peptides, with pandinin 1 belonging to the group of antiba... |
|
|
Single-dose intraperitoneal magainins improve survival in a gram-negative-pathogen septic shock rat model.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46(1) , 101-4, (2002) The therapeutic efficacies of three polycationic peptides selected among the class of the magainins (magainin I, magainin II, and magainin II amide), alone and combined with piperacillin, were investigated in a rat model of septic shock. Rats were given an in... |
|
|
Exploring peptide membrane interaction using surface plasmon resonance: differentiation between pore formation versus membrane disruption by lytic peptides.
Biochemistry 42(2) , 458-66, (2003) Lytic peptides comprise a large group of membrane-active peptides used in the defensive and offensive systems of all organisms. Differentiating between their modes of interaction with membranes is crucial for understanding how these peptides select their targ... |