柯里拉京
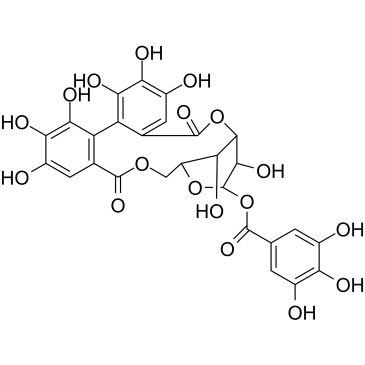
柯里拉京结构式

|
常用名 | 柯里拉京 | 英文名 | corilagin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 23094-69-1 | 分子量 | 634.453 | |
| 密度 | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 1280.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C27H22O18 | 熔点 | >200ºC dec | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 418.8±27.8 °C |
|
Mechanisms of action of corilagin and tellimagrandin I that remarkably potentiate the activity of beta-lactams against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Microbiol. Immunol. 48(1) , 67-73, (2004) Corilagin and tellimagrandin I are polyphenols isolated from the extract of Arctostaphylos uvaursi and Rosa canina L. (rose red), respectively. We have reported that corilagin and tellimagrandin I remarkably reduced the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ... |
|
|
Inhibitory effect of the gallotannin corilagin on dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine ulcerative colitis.
J. Nat. Prod. 76(11) , 2120-5, (2013) The therapeutic effect of corilagin (1) was evaluated in an acute colitis model induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in mice, and the mechanism of action was investigated in this study. Animals were challenged with 2% DSS drinking water for 5 consecutive d... |
|
|
Modulation of PAI-1 and tPA activity and thrombolytic effects of corilagin.
Planta Med. 69(12) , 1109-12, (2003) In this study, Charlton's and Tomihisa's methods were modified to investigate the thrombolytic effect of corilagin from the Chinese herbal plant Phyllanthus urinaria L., as well as its effect on carotid artery patency status. The activity of type 1 plasminoge... |
|
|
Corilagin prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress injury in cultured N9 murine microglia cells.
Neurochem. Int. 59(2) , 290-6, (2011) Oxidative stress plays an important role in neurodegenerative diseases. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated stress in microglia in vivo could result in cellular injuries and preferentially induces neuronal injury. Corilagin, a novel member of the phenolic ... |
|
|
Activity of corilagin on post-parasiticide liver fibrosis in Schistosomiasis animal model.
Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 26(1) , 85-92, (2013) This study investigates the effects and possible molecular mechanisms of corilagin extraction on prevention of Schistosoma japonicum ova-induced granulomas and liver fibrosis. As a result, under a light microscope, when compared to a model group, the corilagi... |
|
|
Hippomanin A from acetone extract of Phyllanthus urinaria inhibited HSV-2 but not HSV-1 infection in vitro.
Phytother Res. 21(12) , 1182-6, (2007) Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea (Euphorbiaceae) is a commonly used traditional medicinal plant in oriental countries and has been reported to possess various biological activities. Previously, the acetone extract and some pure compounds from P. urinaria were foun... |
|
|
Corilagin inhibits the double strand break-triggered NF-kappaB pathway in irradiated microglial cells.
Int. J. Mol. Med. 25(4) , 531-6, (2010) Microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS), are activated by various stimuli. Resting microglia are the basis of normal neurogenesis, while activated microglia may inhibit neurogenesis through the production of pro-inflammatory m... |
|
|
Sensitization of Hep3B hepatoma cells to cisplatin and doxorubicin by corilagin.
Phytother Res. 28(5) , 781-3, (2014) The anticancer action of gallotannins is a well-developed topic. We have demonstrated the in vivo antitumour activity of corilagin on Hep3B hepatoma using the xenograft athymic nude mice model. Here, we further report the potential sensitization of Hep3B hepa... |
|
|
Validated HPLC method for the standardization of Phyllanthus niruri (herb and commercial extracts) using corilagin as a phytochemical marker.
Biomed. Chromatogr. 23(6) , 573-80, (2009) Phyllanthus niruri L., commonly known in Brazil as 'quebra-pedra', has long been used in the treatment of diverse diseases and especially urolithiasis. The therapeutic effects of P. niruri are attributed to various compounds present in the plant, including th... |
|
|
Antiatherogenic effects of phyllanthus emblica associated with corilagin and its analogue.
Yakugaku Zasshi 125(7) , 587-91, (2005) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) is the main etiologic factor in atherogenesis, and antioxidants are accepted as effective treatment of atherosclerosis. The aim of this study was to clarify whether the mechanism of the antiatherogenic effects of the ... |