PJ34盐酸盐
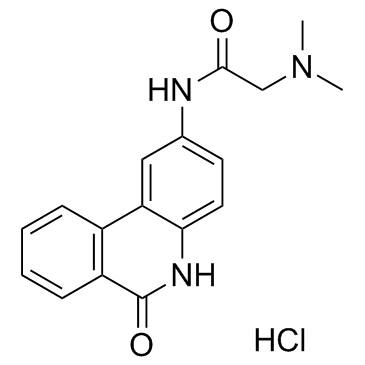
PJ34盐酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | PJ34盐酸盐 | 英文名 | PJ34 HCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 344458-15-7 | 分子量 | 331.80 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 539.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C17H18ClN3O2 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 279.9ºC |
|
Ultraviolet radiation signaling through TLR4/MyD88 constrains DNA repair and plays a role in cutaneous immunosuppression.
J. Immunol. 194(7) , 3127-35, (2015) UV radiation (UVR) induces DNA damage, leading to the accumulation of mutations in epidermal keratinocytes and immunosuppression, which contribute to the development of nonmelanoma skin cancer. We reported previously that the TLR4-MyD88 signaling axis is nece... |
|
|
Poly-ADP-ribosylation of HMGB1 regulates TNFSF10/TRAIL resistance through autophagy.
Autophagy 11(2) , 214-24, (2015) Both apoptosis ("self-killing") and autophagy ("self-eating") are evolutionarily conserved processes, and their crosstalk influences anticancer drug sensitivity and cell death. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that HMGB... |
|
|
Diabetic endothelial dysfunction: the role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation.
Nat. Med. 7 , 108, (2001) Diabetic patients frequently suffer from retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy and accelerated atherosclerosis. The loss of endothelial function precedes these vascular alterations. Here we report that activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is an imp... |
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi induces the reactive oxygen species-PARP-1-RelA pathway for up-regulation of cytokine expression in cardiomyocytes.
J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 285 , 11596-606, (2010) In this study, we demonstrate that human cardiomyocytes (AC16) produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines in response to Trypanosoma cruzi. ROS were primarily produced by mitochondria, some of which diffused to cytosol of infected cardio... |
|
|
Protective effects of PJ34, a novel, potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in in vitro and in vivo models of stroke.
Int. J. Mol. Med. 7 , 255, (2001) Focal cerebral ischemia activates the nuclear protein poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) by single DNA strand breaks which leads to energy depletion and cell necrosis. Deletion or inhibition of PARP protects against ischemic brain injury. Here we examined the... |