α-肌动蛋白
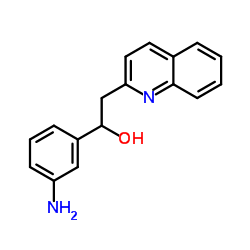
α-肌动蛋白结构式

|
常用名 | α-肌动蛋白 | 英文名 | ALPHA-ACTININ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 11003-00-2 | 分子量 | 264.322 | |
| 密度 | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 461.6±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C17H16N2O | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 233.0±25.9 °C |
|
Androgen therapy reverses injuries caused by ethanol consumption in the prostate: testosterone as a possible target to ethanol-related disorders.
Life Sci. 120 , 22-30, (2015) Chronic ethanol consumption leads to reproductive damages, since it can act directly in the tissues or indirectly, causing a hormonal imbalance. Prostate is a hormone-dependent gland and, consequently, susceptible to ethanol. The potential of testosterone the... |
|
|
Modulation of stretch-induced myocyte remodeling and gene expression by nitric oxide: a novel role for lipoma preferred partner in myofibrillogenesis.
Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 304(10) , H1302-13, (2013) Prolonged hemodynamic load as a result of hypertension eventually leads to maladaptive cardiac adaptation and heart failure. The signaling pathways that underlie these changes are still poorly understood. The adaptive response to mechanical load is mediated b... |
|
|
Interference with the contractile machinery of the fibroblastic chondrocyte cytoskeleton induces re-expression of the cartilage phenotype through involvement of PI3K, PKC and MAPKs.
Exp. Cell Res. 320(2) , 175-87, (2014) Chondrocytes rapidly lose their phenotypic expression of collagen II and aggrecan when grown on 2D substrates. It has generally been observed that a fibroblastic morphology with strong actin-myosin contractility inhibits chondrogenesis, whereas chondrogenesis... |
|
|
The hunt for missing genes.
Science 344(6185) , 687-9, (2014)
|
|
|
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 deletion ameliorates glomerular injury in mice with ACTN4-associated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842(7) , 1028-40, (2014) Renal ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) is upregulated in a subset of human glomerulopathies, including focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), where it may serve to promote ubiquitin pools for degradation of cytotoxic proteins. In the present stud... |
|
|
The non-muscle functions of actinins: an update.
Biochem. J. 459(1) , 1-13, (2014) α-Actinins are a major class of actin filament cross-linking proteins expressed in virtually all cells. In muscle, actinins cross-link thin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres. In non-muscle cells, different actinin isoforms play analogous roles in cross-linki... |
|
|
PARVG gene polymorphism and operational renal allograft tolerance.
Transplant. Proc. 44(9) , 2845-8, (2012) A unique blood transcriptional profile of 49 genes has been previously highlighted that may be used to distinguish drug-free operationally tolerant kidney recipients (TOL) from other kidney recipients with contrasted clinical situations and healthy volunteers... |
|
|
Modeling the assembly of the multiple domains of α-actinin-4 and its role in actin cross-linking.
Biophys. J. 104(3) , 705-15, (2013) The assembly of proteins into multidomain complexes is critical for their function. In eukaryotic nonmuscle cells, regulation of the homodimeric actin cross-linking protein α-actinin-4 (ACTN4) during cell migration involves signaling receptors with intrinsic ... |
|
|
α-actinin1 and 4 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for stress fiber establishment, maintenance and focal adhesion maturation.
Exp. Cell Res. 319(8) , 1124-35, (2013) In polarized, migrating cells, stress fibers are a highly dynamic network of contractile acto-myosin structures composed of bundles of actin filaments held together by actin cross-linking proteins such as α-actinins. As such, α-actinins influence actin cytosk... |
|
|
Z-disc-associated, alternatively spliced, PDZ motif-containing protein (ZASP) mutations in the actin-binding domain cause disruption of skeletal muscle actin filaments in myofibrillar myopathy.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(19) , 13615-26, (2014) The core of skeletal muscle Z-discs consists of actin filaments from adjacent sarcomeres that are cross-linked by α-actinin homodimers. Z-disc-associated, alternatively spliced, PDZ motif-containing protein (ZASP)/Cypher interacts with α-actinin, myotilin, an... |