ML-9盐酸盐
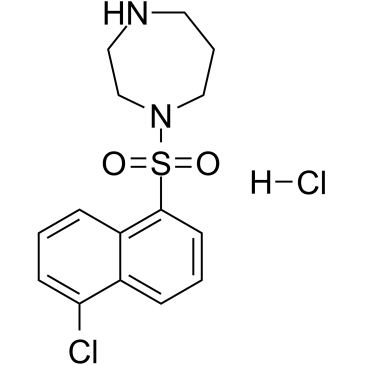
ML-9盐酸盐结构式

|
常用名 | ML-9盐酸盐 | 英文名 | ML-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 105637-50-1 | 分子量 | 361.287 | |
| 密度 | N/A | 沸点 | 508.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C15H18Cl2N2O2S | 熔点 | 196-200ºC | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 261.5ºC |
|
Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(43) , 17253-8, (2013) Phenotypic polarization of macrophages is regulated by a milieu of cues in the local tissue microenvironment. Although much is known about how soluble factors influence macrophage polarization, relatively little is known about how physical cues present in the... |
|
|
Calcium-Dependent Isoforms of Protein Kinase C Mediate Posttetanic Potentiation at the Calyx of Held
Neuron 70(5) , 1005-19, (2011) High-frequency stimulation leads to a transient increase in the amplitude of evoked synaptic transmission that is known as posttetanic potentiation (PTP). Here we examine the roles of the calcium-dependent protein kinase C isoforms PKCα and PKCβ in PTP at the... |
|
|
Linalyl acetate as a major ingredient of lavender essential oil relaxes the rabbit vascular smooth muscle through dephosphorylation of myosin light chain.
J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 48(1) , 850-6, (2006) In a preliminary experiment, we found that lavender essential oil relaxes vascular smooth muscle. Thus, the present experiments were designed to investigate the relaxation mechanism of linalyl acetate as the major ingredient of lavender essential oil in rabbi... |
|
|
A force-activated kinase in a catch smooth muscle.
J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 31(5-6) , 349-58, (2011) Permeabilized anterior byssus retractor muscles (ABRM) from Mytilus edulis were used as a simple system to test whether there is a stretch dependent activation of a kinase as has been postulated for titin and the mini-titin twitchin. The ABRM is a smooth musc... |
|
|
Mechanisms of Rho kinase regulation of vascular reactivity following hemorrhagic shock in rats.
Shock 29(1) , 65-70, (2008) Our previous research showed that Rho kinase took part in the regulation of vascular hyporeactivity after shock. The objective of the present study was to investigate its mechanism. With isolated superior mesenteric artery (SMA) from hemorrhagic shock rats, w... |
|
|
Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase is essential for activation of TRPC5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells.
J. Physiol. 570(Pt 2) , 219-35, (2006) Mammalian homologues of Drosophila transient receptor potential (TRP) proteins are responsible for receptor-activated Ca(2+) influx in vertebrate cells. We previously reported the involvement of intracellular Ca(2+) in the receptor-mediated activation of mamm... |
|
|
Closure of supporting cell scar formations requires dynamic actin mechanisms.
Hear. Res. 232(1-2) , 1-19, (2007) In many vertebrate inner ear sensory epithelia, dying sensory hair cells are extruded, and the apices of surrounding supporting cells converge to re-seal the epithelial barrier between the electrochemically-distinct endolymph and perilymph. These cellular mec... |
|
|
Ca2+-store-dependent and -independent reversal of Stim1 localization and function.
J. Cell Sci. 121(Pt 6) , 762-72, (2008) Stim1 responds to depletion of ER Ca2+ stores by rearranging from tubular structures throughout the ER into punctate structures near the plasma membrane, where it activates Orai store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) channels. However, the mechanism and structural ... |
|
|
Gi-coupled receptors mediate phosphorylation of CPI-17 and MLC20 via preferential activation of the PI3K/ILK pathway.
Biochem. J. 396(1) , 193-200, (2006) Sustained smooth-muscle contraction or its experimental counterpart, Ca2+ sensitization, by G(q/13)-coupled receptor agonists is mediated via RhoA-dependent inhibition of MLC (myosin light chain) phosphatase and MLC20 (20 kDa regulatory light chain of myosin ... |
|
|
Differential roles for STIM1 and STIM2 in store-operated calcium entry in rat neurons.
PLoS ONE 6(4) , e19285, (2011) The interaction between Ca(2+) sensors STIM1 and STIM2 and Ca(2+) channel-forming protein ORAI1 is a crucial element of store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) in non-excitable cells. However, the molecular mechanism of SOCE in neurons remains unclear. We address... |