Juvenile Hormone III
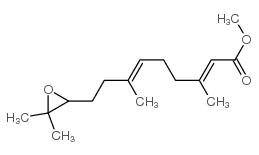
Juvenile Hormone III结构式

|
常用名 | Juvenile Hormone III | 英文名 | Juvenile Hormone III (trans-trans-10,11-Epoxyfarnesenic Acid methyl ester) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 24198-95-6 | 分子量 | 266.37600 | |
| 密度 | 0.966g/cm3 | 沸点 | 348.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C16H26O3 | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 144.9ºC |
|
Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometric quantitation of juvenile hormone III in whole body extracts of the Formosan subterranean termite.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 877(27) , 3175-80, (2009) Juvenile hormone (JH) III is responsible for control of a variety of insect physiological and developmental states, including caste differentiation of the Formosan subterranean termite (Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki). We report here a simplified, efficient s... |
|
|
Juvenile hormone prevents 20-hydroxyecdysone-induced metamorphosis by regulating the phosphorylation of a newly identified broad protein.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(38) , 26630-41, (2014) The steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) initiates insect molting and metamorphosis. By contrast, juvenile hormone (JH) prevents metamorphosis. However, the mechanism by which JH inhibits metamorphosis remains unclear. In this study, we propose that JH in... |
|
|
Regulation of Gene Expression Patterns in Mosquito Reproduction.
PLoS Genet. 11 , e1005450, (2015) In multicellular organisms, development, growth and reproduction require coordinated expression of numerous functional and regulatory genes. Insects, in addition to being the most speciose animal group with enormous biological and economical significance, rep... |
|
|
Mapping of the Sequences Directing Localization of the Drosophila Germ Cell-Expressed Protein (GCE).
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133307, (2015) Drosophila melanogaster germ cell-expressed protein (GCE) belongs to the family of bHLH-PAS transcription factors that are the regulators of gene expression networks that determine many physiological and developmental processes. GCE is a homolog of D. melanog... |
|
|
Knockout silkworms reveal a dispensable role for juvenile hormones in holometabolous life cycle.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , E4226-35, (2015) Insect juvenile hormones (JHs) prevent precocious metamorphosis and allow larvae to undergo multiple rounds of status quo molts. However, the roles of JHs during the embryonic and very early larval stages have not been fully understood. We generated and chara... |
|
|
Methyl farnesoate plays a dual role in regulating Drosophila metamorphosis.
PLoS Genet. 11(3) , e1005038, (2015) Corpus allatum (CA) ablation results in juvenile hormone (JH) deficiency and pupal lethality in Drosophila. The fly CA produces and releases three sesquiterpenoid hormones: JH III bisepoxide (JHB3), JH III, and methyl farnesoate (MF). In the whole body extrac... |
|
|
Juvenile hormone (JH) esterase activity but not JH epoxide hydrolase activity is downregulated in larval Adoxophyes honmai following nucleopolyhedroviruses infection.
J. Insect Physiol. 80 , 71-80, (2015) Juvenile hormones (JHs) and ecdysteroids are critical insect developmental hormones. JH esterase (JHE) and JH epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) are JH-selective enzymes that metabolize JH and thus regulate the titer of JH. Baculoviruses are known to alter host endocri... |
|
|
Microarray analysis of juvenile hormone response in Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells.
J. Insect Sci. 10 , 66, (2010) A microchip array encompassing probes for 14,010 genes of Drosophila melanogaster was used to analyze the effect of juvenile hormone (JH) on genome-wide gene expression. JH is a member of a group of insect hormones involved in regulating larval development an... |
|
|
Socio-environmental and endocrine influences on developmental and caste-regulatory gene expression in the eusocial termite Reticulitermes flavipes.
BMC Mol. Biol. 11 , 28, (2010) Strict regulation of caste differentiation, at the molecular level, is thought to be important to maintain social structure in insect societies. Previously, a number of extrinsic and intrinsic factors have been shown to influence caste composition in termite ... |
|
|
Structural and RNAi characterization of the German cockroach lipophorin receptor, and the evolutionary relationships of lipoprotein receptors.
BMC Mol. Biol. 8 , 53, (2007) Lipophorin receptors (LpRs) have been described in a number of insects, but functional studies have been reported only in locusts and mosquitoes. The aim of the present work was to characterize the LpR of the cockroach Blattella germanica, not only molecularl... |