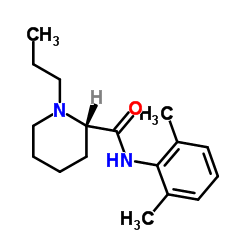
Ropivacaine Hydrochloride

Ropivacaine Hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Ropivacaine Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 98717-15-8 | Molecular Weight | 310.862 | |
| Density | 1.044 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 410.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H27ClN2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 201.9ºC | |
Use of Ropivacaine HydrochlorideRopivacaine hydrochloride is an inhibitor of K2P (two-pore domain potassium channel) TREK-1 with an IC50 of 402.7 μM. |
| Name | (S)-ropivacaine hydrochloride (anhydrous) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ropivacaine hydrochloride is an inhibitor of K2P (two-pore domain potassium channel) TREK-1 with an IC50 of 402.7 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 402.7 μM (K2P TREK-1)[1] |
| In Vitro | Ropivacaine hydrochloride shows reversible inhibition of TREK-1 channels in a concentration-dependent manner. The half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of Ropivacaine hydrochloride is 402.7±31.8 μM.. Hill coefficient is 0.89 for Ropivacaine hydrochloride[1]. |
| In Vivo | Epidural injections of Ropivacaine hydrochloride (60, 180 and 600 μg) produce immediate and reversible motor paralysis. The motor blockade effect is dose-dependent, with paralysis duration of 4.6, 14.6 and 29.5 mins, respectively. Epidural Ropivacaine hydrochloride sustained release suspension also produces significant blockade of mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia by 59.5% and 70.9%, respectively (P<0.05). Ropivacaine hydrochloride sustained release suspension also produces a mild antinociception (response to heat stimulus) but longer anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects, with biological half-lives of 6.4±2.5 hrs and 6.8±2.9 hrs, respectively (P<0.05). Multiple daily epidural administration of Ropivacaine hydrochloride sustained release suspension prolongs the preemptive effects (P<0.05)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | COS-7 cells are cultured in a 5 % CO2 humidified incubator at 37°C in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium containing 10 % heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, and 1 % penicillin/streptomycin (100 U/mL and 100 μg/mL). The effect of Ropivacaine hydrochloride (10, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) on TREK-1 channels are investigated in COS-7 cells by using the whole cell patch clamp technique with a voltage ramp protocol ranging from -100 to 100 mV for 200 ms from a holding potential of -70 mV[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Adult male Wistar rats (240±20 g body weight) are used in this study. Animals are housed four per cage with thick sawdust bedding at standard room temperature, under a 12/12 hrs reversed light-dark cycle (7:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m.) at a constant temperature of 22±2°C. All rats receive food and water ad libitum. For epidural administration of Ropivacaine hydrochloride, a polyethylene catheter is implanted into the epidural space. One hundred microliters of 0.2% Ropivacaine hydrochloride injection, 0.2% Ropivacaine hydrochloride sustained release suspension or saline is slowly injected for 30 secs through the epidural catheter, followed by 10 μL of sterile saline[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.044 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 410.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H27ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 310.862 |
| Flash Point | 201.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 310.181183 |
| PSA | 32.34000 |
| LogP | 4.31930 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|
|
~99% 
Ropivacaine Hyd... CAS#:98717-15-8 |
| Literature: DISHMAN PHARMACEUTICALS AND CHEMICALS LTD.; PLUIM, Henk Patent: WO2007/123405 A1, 2007 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 10-11 ; |
|
~% 
Ropivacaine Hyd... CAS#:98717-15-8 |
| Literature: WO2010/84516 A1, ; Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~% 
Ropivacaine Hyd... CAS#:98717-15-8 |
| Literature: Acta Chemica Scandinavica, Series B: Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry, , vol. 41, # 10 p. 757 - 761 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| (2S)-N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-1-propyl-2-piperidincarboxamide hydrochloride |
| Ropivacaine hydrochl |
| piperidine-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| (S)-Ropivacaine Hydrochloride |
| ROPIVCACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE |
| UNII-35504LBE2T |
| L-N-n-propylpipecolic acid-2,6-xylidide hydrochloride |
| S-ROPIVACAINE HCL |
| REACTIVE YELLOW 145 |
| (S)-N-n-propyl-(2,6)-dimethylphenyl-2-piperidine carboxamide hydrochloride |
| ROPIVACAINEHCL |
| (S)-1-propyl-2-piperidylformo-2',6'-xylidide hydrochloride |
| Piperidine-3-Carboxamide Hydrochloride |
| (S)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-1-propyl-2-piperidinecarboxamide monohydrochloride |
| n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-propyl-piperidine-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| Ropivacaine HCL |
| L-ropivacaine HCl |
| (S)-(-)-1-propyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide hydrochloride |
| 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-propyl-, (2S)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Naropin |
| Ropivacainehydrochloride |
| Ropivacaine monohydrochloride |
| Ropivacaine Hydrochloride |
| Ropivacaine mesilate |
| (S)ROPIVACAINE HCL |
| (s)-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-propylpiperidine-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| (2S)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1-propyl-pipecolinamide hydrochloride |
| (2S)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-1-propylpiperidine-2-carboxamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
| L-ropivacaine hydrochloride |
| ROPIVACAINE |
| 2-PIPERIDINECARBOXAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE |
| PIPERIDINE-2-CARBOXAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE API |
| ROPIVACAINE 1-HYDRATE |
| S-ROPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE |
| (2S)-2-[(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)carbamoyl]-1-propylpiperidinium chloride |
| MFCD02102164 |


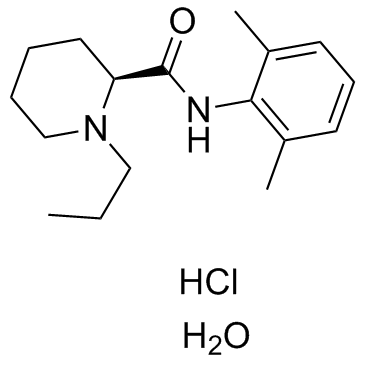 CAS#:132112-35-7
CAS#:132112-35-7