Aspergillus acid protease
Aspergillus acid protease structure
|
Common Name | Aspergillus acid protease | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9025-49-4 | Molecular Weight | 232.235 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 413.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
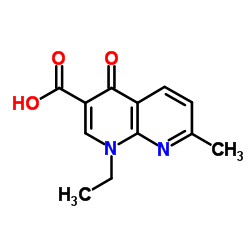
| Molecular Formula | C12H12N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 203.6±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Aspergillus acid proteaseAspergillopepsin I (Aspergillus acid protease) is an aspartic endopeptidase that catalyses the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins, with broad specificity[1]. |
| Name | Proteinase, Aspergillus acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Aspergillopepsin I (Aspergillus acid protease) is an aspartic endopeptidase that catalyses the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in proteins, with broad specificity[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 413.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C12H12N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 232.235 |
| Flash Point | 203.6±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 232.084793 |
| LogP | 1.19 |
| Appearance of Characters | white powder |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.605 |
| InChIKey | RUWHAENIXFIHPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1OC(C)=C(COC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COC(=O)C=CC(=O)OC)O1.COC(=O)C=CC(=O)OCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)OCCCn1ccnc1.COC(=O)C=CC(=O)OCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)OCCN1CCCCC1.COC(=O)C=CC(=O)OCC(C)(C)C(O)C(=O)OCOC(=O)C(C)C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | 5-20 mg/mL |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 37/38-41-42-36/37/38-42/43-20 |
| Safety Phrases | 23-24-26-36/37/39-36/37-22-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UK9595000 |
|
[Modification of two tyrosine residues in aspergillopepsin A by p-nitrophenyldiazonium chloride].
Biokhimiia 46(2) , 369-75, (1981) p-Nitrophenyldiazonium chloride was found to modify the Tyr-75 and Tyr-189 residues in aspergillopepsin A. Incubation of the protein with a 45-fold molar excess of the reagent at pH 5,2 results in the... |
|
|
Sequences from the aspergillopepsin PEP gene of Aspergillus fumigatus: evidence on their use in selective PCR identification of Aspergillus species in infected clinical samples.
FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 25(3) , 255-64, (1999) In immunodeficient patients, Aspergillus species emerge as circumstantial pathogens. Aspergillus fumigatus is a distant first among the pathogenic aspergilli, which cause deep-seated mycoses. Sequence... |
|
|
The site of diazoacetyl inhibitor attachment to acid proteinase of Aspergillus awamori--an analog of penicillopepsin and pepsin.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 49(4) , 1075-81, (1972)
|
| 1,8-Naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid, 1-ethyl-1,4-dihydro-7-methyl-4-oxo- |
| 1-Ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
| Ethyl-7-methyl-1,8-naphthyridin-4-one-3-carboxylic Acid |
| T66 BV EN GNJ CVQ E2 H1 |
| Acide 1-etil-7-metil-1,8-naftiridin-4-one-3-carbossilico |
| NegGram |
| WIN-18320 |
| WINTOMYLON |
| Acide nalidixico |
| nalidixic acid |
| Aspergillus acid protease |
| EINECS 232-796-2 |

