Neurokinin B trifluoroacetate salt
Neurokinin B trifluoroacetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Neurokinin B trifluoroacetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86933-75-7 | Molecular Weight | 1210.42000 | |
| Density | 1.313 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1646ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C55H79N13O14S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 949.3ºC | |
Use of Neurokinin B trifluoroacetate saltNeurokinin B belongs to the tachykinin family of peptides. Neurokinin B binds a family of GPCRs—including neurokinin receptor 1 (NK1R), NK2R, and NK3R-to mediate their biological effect. |
| Name | Neurokinin B (human, porcine) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Neurokinin B belongs to the tachykinin family of peptides. Neurokinin B binds a family of GPCRs—including neurokinin receptor 1 (NK1R), NK2R, and NK3R-to mediate their biological effect. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Neurokinin receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | Neurokinin B (NKB) belongs to the tachykinin family of peptides that initially included the neuropeptides substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NKA), and NKB and more recently, endokinins and hemokinins. Tachykinins bind a family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)-including neurokinin receptor 1 (NK1R), NK2R, and NK3R-to mediate their biological effect[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Navarro VM. Interactions between kisspeptins and neurokinin B. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;784:325-47. |
| Density | 1.313 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1646ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C55H79N13O14S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 1210.42000 |
| Flash Point | 949.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 1209.53000 |
| PSA | 484.89000 |
| LogP | 3.32120 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| InChIKey | NHXYSAFTNPANFK-HDMCBQFHSA-N |
| SMILES | CSCCC(NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(Cc1cnc[nH]1)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(N)CC(=O)O)C(C)C)C(N)=O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Current and future applications of GnRH, kisspeptin and neurokinin B analogues.
Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 9(8) , 451-66, (2013) Reproductive hormones affect all stages of life from gamete production, fertilization, fetal development and parturition, neonatal development and puberty through to adulthood and senescence. The repr... |
|
|
Neuroanatomy of the kisspeptin signaling system in mammals: comparative and developmental aspects.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 784 , 27-62, (2013) Our understanding of kisspeptin and its actions depends, in part, on a detailed knowledge of the neuroanatomy of the kisspeptin signaling system in the brain. In this chapter, we will review our curre... |
|
|
Alteration in neonatal nutrition causes perturbations in hypothalamic neural circuits controlling reproductive function.
J. Neurosci. 32(33) , 11486-94, (2012) It is increasingly accepted that alterations of the early life environment may have lasting impacts on physiological functions. In particular, epidemiological and animal studies have indicated that ch... |
| Neurokinin B NKB |
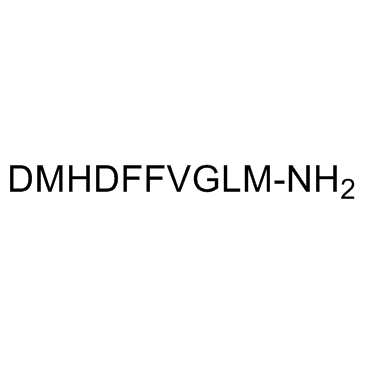
| DMHDFFVGLM-NH2 |
| NKB |
| NEUROKININ K |
| MFCD00133665 |
| NEUROKININ B |
| NEUROMEDIN K |

