Phenformin (hydrochloride)
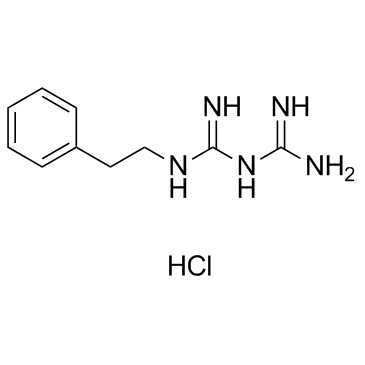
Phenformin (hydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | Phenformin (hydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 834-28-6 | Molecular Weight | 241.721 | |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 413.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16ClN5 | Melting Point | 175-178ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 204ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Phenformin (hydrochloride)Phenformin (hydrochloride) is a hydrochloride salt of phenformin that is an anti-diabetic drug from the biguanide class, can activate AMPK activity. |
| Name | Phenformin hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Phenformin (hydrochloride) is a hydrochloride salt of phenformin that is an anti-diabetic drug from the biguanide class, can activate AMPK activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
AMPK |
| In Vitro | Phenformin stimulates the phosphorylation and activation of AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2 without altering LKB1 activity[1]. Phenformin increases AMPK activity and phosphorylation in the isolated heart, the increase in AMPK activity is always preceded by and correlated with increased cytosolic [AMP][2]. Phenformin is a 50-fold more potent inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I than metformin. Phenformin robustly induces apoptosis in LKB1 deficient NSCLC cell lines. Phenformin at 2 mM similarly induces AMPK signaling as shown by increased P-AMPK and P-Raptor levels. Phenformin induces higher levels of cellular stress, triggering induction of P-Ser51 eIF2α and its downstream target CHOP, and markers of apoptosis at later times. Phenformin induces a significant increase in survival and therapeutic response in KLluc mice following long-term treatment[3]. Phenformin and AICAR increases AMPK activity in H441 cells in a dose-dependent fashion, stimulating the kinase maximally at 5-10 mm and 2 mm, respectively. Phenformin significantly decreases basal ion transport (measured as short circuit current) across H441 monolayers by approximately 50% compared with that of controls. Phenformin and AICAR significantly reduce amiloride-sensitive transepithelial Na+ transport compared with controls. Phenformin and AICAR suppress amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport across H441 cells via a pathway that includes activation of AMPK and inhibition of both apical Na+ entry through ENaC and basolateral Na+ extrusion via the Na+,K+-ATPase[4]. Phenformin-treated rats reveals a tendency towards a decrease in blood insulin level (radioimmunoassay)[5]. |
| In Vivo | Phenformin increases levels of P-eIF2α and its target BiP/Grp78 in normal lung as well as in lung tumors of mice[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Total AMPK activity is measured using the method of Dagher et al. AMPK activity is quantified in the resuspended pellet as incorporation of 32P from [γ-32P]ATP (10 GBq/mmol) into a synthetic peptide with the specific target sequence for AMPK, the SAMS peptide. Radioactivity is measured using a liquid scintillation counter. Protein content in the solution containing the resupended (NH4)2SO4 pellet is determined using the Bradford method. |
| References |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 413.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 175-178ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H16ClN5 |
| Molecular Weight | 241.721 |
| Flash Point | 204ºC |
| Exact Mass | 241.109421 |
| PSA | 97.78000 |
| LogP | 2.72010 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | >=10 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S36 |
| RIDADR | 2811.0 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DU2200000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Hydrogen sulfide mitigates hyperglycemic remodeling via liver kinase B1-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843(12) , 2816-26, (2014) Hyperglycemia (HG) reduces AMPK activation leading to impaired autophagy and matrix accumulation. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) treatment improves HG-induced renovascular remodeling however, its mechanism re... |
|
|
Lactic acidosis treatment by nanomole level of spermidine in an animal model.
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 70(2) , 514-8, (2014) Lactic acidosis occurs in a number of clinical conditions, e.g. in surgeries, orthotopic liver transplant, and anesthetic agent administration, which has deleterious effects on the patient's survival.... |
| Phenformin hydrochloride |
| Phenformini Hydrochloride |
| Insora |
| meltrol |
| phenforminhclno.9113 |
| Imidodicarbonimidic diamide, N-(2-phenylethyl)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Glucopostin |
| Phenformine HCL |
| dbi-td |
| β-PEBG HCl |
| DBI monohydrochloride |
| usafvi-6 |
| MFCD00035039 |
| Phenformin HCl |
| PhenforMin HCl API |
| UNII-91XC93EU03 |
| EINECS 212-637-3 |
| Insoral |
| N-(2-Phenylethyl)imidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride (1:1) |
| N-Phenethylbiguanide hydrochloride |
| 1-(2-Phenylethyl)biguanide hydrochloride |
| N'-b-Phenethylformamidinyliminourea Hydrochloride |
| Phenformin (hydrochloride) |
| 1,1-Benzylmethylbiguanide hydrochloride |
 CAS#:114-86-3
CAS#:114-86-3
