N-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid
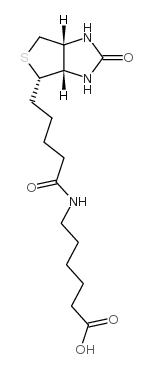
N-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | N-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72040-64-3 | Molecular Weight | 357.46800 | |
| Density | 1.2g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 721.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H27N3O4S | Melting Point | 220-230ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 390ºC | |
Use of N-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acidN-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid (N-(+)-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid) can be used to perform biotinylation[1]. |
| Name | N-Biotinylcaproic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid (N-(+)-Biotinyl-6-aminohexanoic acid) can be used to perform biotinylation[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Synthesis of p-nitrophenyl N-acetyllactosaminide with β-D-galactosidase, chemical reduction of the p-nitrophenyl group, and sialylation with sialyltransferase. The p-aminophenyl glycosides are then successfully biotin-labeled through the coupling with N-(+)-biotinyl-6- aminohexanoic acid to afford biotinylated oligosaccharides with an aminohexanosyl group and phenyl group as the spacers between the biotin and glycan[1]. The SERS (surface-enhanced Raman scattering) of cyclohexyl isocyanide that silver nanoparticles modified with N-(+)-biotinyl-6-aminocaproic acid and cyclohexyl isocyanide can be anchored on a separate biotinylated substrate via the avidin-biotin interaction[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 721.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 220-230ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H27N3O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 357.46800 |
| Flash Point | 390ºC |
| Exact Mass | 357.17200 |
| PSA | 132.83000 |
| LogP | 2.52190 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.532 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | F: Flammable; |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~76% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: Skander, Myriem; Humbert, Nicolas; Collot, Jerome; Gradinaru, Julieta; Klein, Gerard; Loosli, Andreas; Sauser, Jerome; Zocchi, Andrea; Gilardoni, Francois; Ward, Thomas R. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004 , vol. 126, # 44 p. 14411 - 14418 |
|
~79% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: Shi, Haibin; Liu, Kai; Xu, Ashley; Yao, Shao Q. Chemical Communications, 2009 , # 33 p. 5030 - 5032 |
|
~% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: US2012/232262 A1, ; Page/Page column 3 ; |
|
~% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: US2012/232262 A1, ; |
|
~% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, , vol. 43, # 4 p. 309 - 322 |
|
~% 
N-Biotinyl-6-am... CAS#:72040-64-3 |
| Literature: Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, , vol. 43, # 4 p. 309 - 322 |
|
In vivo labeling of Escherichia coli cell envelope proteins with N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of biotin. Bradburne JA, Godfrey P, et al.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59 , 663-668, (2993)
|
|
|
(-)-7'-Isothiocyanato-11-hydroxy-1',1'-dimethylheptylhexahydrocannabinol (AM841), a high-affinity electrophilic ligand, interacts covalently with a cysteine in helix six and activates the CB1 cannabinoid receptor.
Mol. Pharmacol. 68 , 1623-35, (2005) The CB1 cannabinoid receptor has been shown to play important physiological roles in the central nervous system, as well as peripherally, and is a target for development of therapeutic medications. To... |
|
|
microAg particle-based molecular sensing/recognition via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 22 , 1000-1005, (2007) In this study, we demonstrate that powders of commercially available 2-microm-sized Ag (microAg) can be used as a core material for constructing molecular sensing/recognition units operating via surfa... |
| 6-[5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoylamino]hexanoic acid |


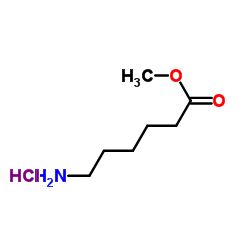
 CAS#:89889-51-0
CAS#:89889-51-0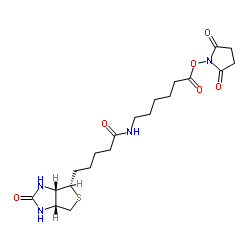 CAS#:72040-63-2
CAS#:72040-63-2
