N-Nitroso-N-methylurea
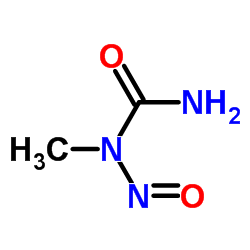
N-Nitroso-N-methylurea structure
|
Common Name | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 684-93-5 | Molecular Weight | 103.080 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 164.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5N3O2 | Melting Point | 119-124°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 53.1±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of N-Nitroso-N-methylureaN-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU;MNU;NMH) is a potent carcinogen, mutagen and teratogenand. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea is a direct-acting alkylating agent that interacts with DNA. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea targets multiple animal organs to cause various cancer and/or degenerative disease. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea is also a precursor in the synthesis of diazomethane[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | N-methyl-N-nitrosourea |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU;MNU;NMH) is a potent carcinogen, mutagen and teratogenand. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea is a direct-acting alkylating agent that interacts with DNA. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea targets multiple animal organs to cause various cancer and/or degenerative disease. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea is also a precursor in the synthesis of diazomethane[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU; 5 μM) treatment increases the cellular NF-κB activity in human malignant keratinocytes. N-Nitroso-N-methylurea also increases the amount of I-κBα phosphorylation[5]. |
| In Vivo | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU) gives intravenously to rats at age 50 days induced mammary carcinomas in 89% of BUF/N, 73% of Sprague-Dawley, and 89% of F344 females. Latent periods are, respectively, 77, 86, and 94 days. Doubling times of NMU-induced primary and transplanted carcinomas are similar to 7 days. Cachexia ensues at the 5th week from the onset of the first tumor. When the tumor is larger than 15 g, hypercalcemia is usually observed[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 164.3±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 119-124°C |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 103.080 |
| Flash Point | 53.1±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 103.038177 |
| PSA | 75.76000 |
| LogP | -0.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong acids. |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H228-H301-H350-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P210-P301 + P310-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable |
| Risk Phrases | R45;R46;R61;R11;R25 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S24/25-S22 |
| RIDADR | UN 1325 4.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | YT7875000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
~92% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Iranpoor, Nasser; Firouzabadi, Habib; Pourali, Ali Reza Synthetic Communications, 2005 , vol. 35, # 11 p. 1517 - 1526 |
|
~% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Current Science, , vol. 12, p. 228 Chem.Abstr., , p. 2006 Journal of the Chemical Society, , p. 1214 Chemische Berichte, , vol. 73, p. 607 |
|
~% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 38, p. 1325 - 1329 |
|
~% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 73, p. 607 Org. Synth. Coll. Vol. II<1943>461 Angewandte Chemie, , vol. 46, p. 48 Angewandte Chemie, , vol. 43, p. 445 |
|
~% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 73, p. 607 Org. Synth. Coll. Vol. II<1943>461 Angewandte Chemie, , vol. 46, p. 48 Angewandte Chemie, , vol. 43, p. 445 |
|
~% 
N-Nitroso-N-met... CAS#:684-93-5 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , vol. 253, p. 6 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
A novel toxicogenomics-based approach to categorize (non-)genotoxic carcinogens.
Arch. Toxicol. 89 , 2413-27, (2015) Alternative methods to detect non-genotoxic carcinogens are urgently needed, as this class of carcinogens goes undetected in the current testing strategy for carcinogenicity under REACH. A complicatin... |
|
|
Optimal dose selection of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea for the rat comet assay to evaluate DNA damage in organs with different susceptibility to cytotoxicity.
Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 786-788 , 129-36, (2015) The in vivo rodent alkaline comet assay (comet assay) is a promising technique to evaluate DNA damage in vivo. However, there is no agreement on a method to evaluate DNA damage in organs where cytotox... |
|
|
Multiple programmed cell death pathways are involved in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced photoreceptor degeneration.
Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 253 , 721-31, (2015) To identify programmed cell death (PCD) pathways involved in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)-induced photoreceptor (PR) degeneration.Adult C57BL/6 mice received a single MNU i.p. injection (60 mg/kg body... |
| EINECS 211-678-4 |
| 1-Methyl-1-nitrosourea |
| Urea, N-methyl-N-nitroso- |
| N-nitroso-N-methylurea |
| MFCD00014794 |
![Acetamide,N-[(methylamino)carbonyl]- structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/167/623-59-6.png)
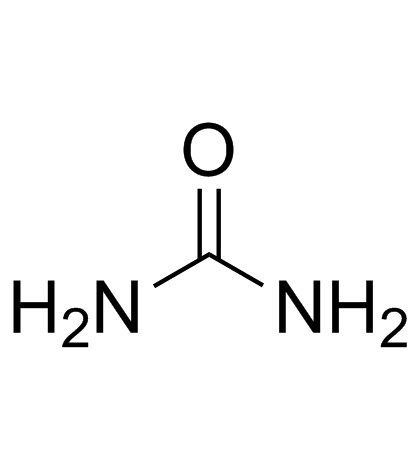
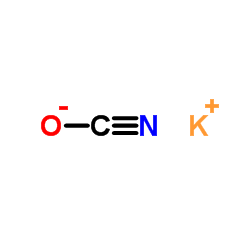
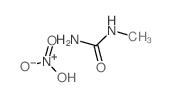
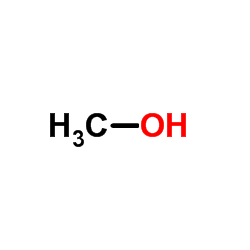 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1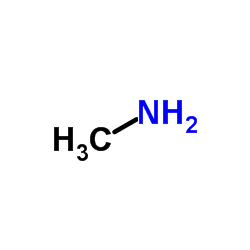 CAS#:74-89-5
CAS#:74-89-5 CAS#:538-32-9
CAS#:538-32-9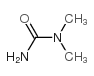 CAS#:598-94-7
CAS#:598-94-7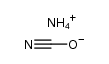 CAS#:22981-32-4
CAS#:22981-32-4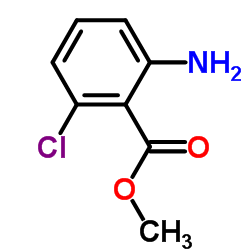 CAS#:41632-04-6
CAS#:41632-04-6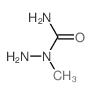 CAS#:22718-48-5
CAS#:22718-48-5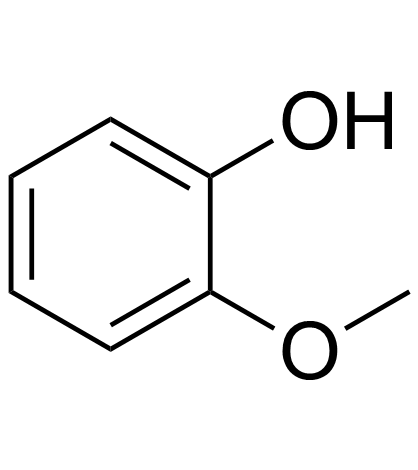 CAS#:90-05-1
CAS#:90-05-1