Dicyclomine hydrochloride
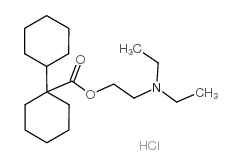
Dicyclomine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Dicyclomine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 345.94800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 399.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H36ClNO2 | Melting Point | 164-166ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 116.5ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Dicyclomine hydrochlorideDicyclomine hydrochloride is a potent and orally active muscarinic cholinergic receptors antagonist. Dicyclomine hydrochloride shows high affinity for muscarinic M1 receptor subtype (Ki=5.1 nM) and M2 receptor subtype (Ki=54.6 nM) in brush-border membrane and basal plasma membranes, respectively[1]. Dicyclomine is an antispasmodic agent and relieves smooth muscle spasm of the gastrointestinal tract in vivo[2]. |
| Name | dicyclomine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dicyclomine hydrochloride is a potent and orally active muscarinic cholinergic receptors antagonist. Dicyclomine hydrochloride shows high affinity for muscarinic M1 receptor subtype (Ki=5.1 nM) and M2 receptor subtype (Ki=54.6 nM) in brush-border membrane and basal plasma membranes, respectively[1]. Dicyclomine is an antispasmodic agent and relieves smooth muscle spasm of the gastrointestinal tract in vivo[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 5.1 nM (muscarinic M1 receptor subtype in brush-border membrane) Ki: 54.6 nM (muscarinic M2 receptor subtype in basal plasma membrane[1] |
| In Vivo | Dicyclomine hydrochloride (intraperitoneal injection; 8 mg/kg; daily) exacerbates the cognitive impairments in all the measurements. In addition, the memory impairments are worse in dicyclomine-treated 3xTg-AD mice compared to dicyclomine-treated NonTg mice[2]. Dicyclomine hydrochloride (intraperitoneal injection; 2.0, 4.0, and 8.0 mg/kg; 7 days) produces a highly significant effect on performance in the paired-associates learning (PAL) task in mice.And systemic treatment at lower doses show behavioral impairments in mice in spatial tasks[3]. Animal Model: C57Bl/6 mice[1] Dosage: 2.0, 4.0, and 8.0 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; 7 days Result: Produced impairments due to actions of the agent outside of the hippocampus. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 399.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 164-166ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H36ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 345.94800 |
| Flash Point | 116.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 345.24300 |
| PSA | 29.54000 |
| LogP | 5.20420 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | off-white |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22-36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DT7350000 |
|
Treating morning sickness in the United States--changes in prescribing are needed.
Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 211(6) , 602-6, (2014) Presently, 97.7% of prescriptions for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy in the United States are with medications not labeled for use in pregnancy, not indicated for nausea and vomitin... |
|
|
Recommendations for the management of Acanthamoeba keratitis.
J. Med. Microbiol. 63(Pt 5) , 770-1, (2014)
|
| 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 1-cyclohexylcyclohexane-1-carboxylate,hydrochloride |
| Dicyclomine, Hydrochloride |