(D-Ala2)-Leu-Enkephalin
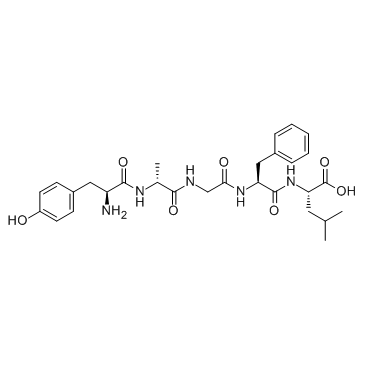
(D-Ala2)-Leu-Enkephalin structure
|
Common Name | (D-Ala2)-Leu-Enkephalin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64963-01-5 | Molecular Weight | 569.649 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 991.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N5O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 553.7±34.3 °C | |
Use of (D-Ala2)-Leu-Enkephalin[D-Ala2]leucine-enkephalin, a delta opioid agonist, is a degradation resistant long-acting Leu-enkephalin. Sequence: Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-Leu. |
| Name | 2-[[2-[[2-[2-[[2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]acetyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | [D-Ala2]leucine-enkephalin, a delta opioid agonist, is a degradation resistant long-acting Leu-enkephalin. Sequence: Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-Leu. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 991.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N5O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 569.649 |
| Flash Point | 553.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 569.284973 |
| PSA | 199.95000 |
| LogP | 2.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.582 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Agonist activation of p42 and p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases following expression of the mouse delta opioid receptor in Rat-1 fibroblasts: effects of receptor expression levels and comparisons with G-protein activation.
Biochem. J. 320 , 227-235, (1996) Rat-1 fibroblasts were transfected with a cDNA encoding the mouse delta opioid receptor. Two separate clones, D2 (which expressed some 6 pmol of the receptor/mg of membrane protein) and DOE (which exp... |
|
|
Activation of mu- and delta-opioid receptors causes presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic excitation in neocortical neurons.
Anesthesiology 93 , 1053-1063, (2000) The mechanism underlying the depressant effect of opioids on neuronal activity within the neocortex is still not clear. Three modes of action have been suggested: (1) inhibition by activation of posts... |
|
|
Direct excitatory opiate effects mediated by non-synaptic actions on rat medial vestibular neurons.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 262 , 99-106, (1994) Opiates increase firing of rat medial vestibular nucleus neurons. We have attempted to determine the mechanism of these excitatory opiate actions by extracellular recording of neuronal activity with i... |
| N-[N-[N-(N-L-tyrosyl-D-alanyl)glycyl]-L-phenylalanyl]-L-leucine |
| D-Ala(2)-Leu(5)-Enk |
| TYR-D-ALA-GLY-PHE-LEU |
| Leucine, tyrosylalanylglycylphenylalanyl- |
| D-Ala2,D-Leu5-enkephalin |
| Tyrosylalanylglycylphenylalanylleucine |
| D-ALA2-LEU5-ENKEPHALIN |
| D-(Ala)2-leucine enkephalin |
| [D-Ala2]-Leucine enkephalin |
| Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-Leu |
| H-TYR-D-ALA-GLY-PHE-LEU-OH |
| L-Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-L-Phe-L-Leu-OH |
| (D-ALA2)-LEU-ENKEPHALIN |
| Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-Leu-OH |
| (D-alanine2)leucine enkephalin |
| Pentapeptide-18 |
| Leuphasyl |
| [D-Ala2]leucine-enkephalin |

