CHOLESTERYL LINOLEATE
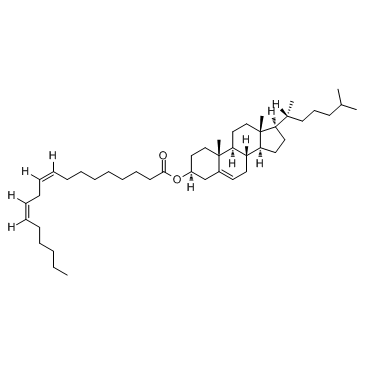
CHOLESTERYL LINOLEATE structure
|
Common Name | CHOLESTERYL LINOLEATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 604-33-1 | Molecular Weight | 649.084 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 677.3±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H76O2 | Melting Point | 42ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 364.0±16.0 °C | |
Use of CHOLESTERYL LINOLEATECholesteryl linoleate is shown to be the major cholesteryl ester contained in LDL and atherosclerotic lesions. |
| Name | cholesteryl linoleate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cholesteryl linoleate is shown to be the major cholesteryl ester contained in LDL and atherosclerotic lesions. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 677.3±44.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 42ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C45H76O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 649.084 |
| Flash Point | 364.0±16.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 648.584534 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 18.17 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.517 |
| InChIKey | NAACPBBQTFFYQB-XNTGVSEISA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC1CCC2(C)C(=CCC3C2CCC2(C)C(C(C)CCCC(C)C)CCC32)C1 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~95% 
CHOLESTERYL LIN... CAS#:604-33-1 |
| Literature: Shimada, Yuji; Hirota, Yoshinori; Baba, Takashi; Sugihara, Akio; Moriyama, Shigeru; Tominaga, Yoshio; Terai, Tadamasa JAOCS, Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 1999 , vol. 76, # 6 p. 713 - 716 |
|
~% 
CHOLESTERYL LIN... CAS#:604-33-1 |
| Literature: Biochemische Zeitschrift, , vol. 220, p. 304,308, 321 |
|
~% 
CHOLESTERYL LIN... CAS#:604-33-1 |
| Literature: Biochemische Zeitschrift, , vol. 220, p. 304,308, 321 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Autophagy facilitates secretion and protects against degeneration of the Harderian gland.
Autophagy 11(2) , 298-313, (2015) The epithelial derived Harderian gland consists of 2 types of secretory cells. The more numerous type A cells are responsible for the secretion of lipid droplets, while type B cells produce dark granu... |
|
|
A rapid and precise method for quantification of fatty acids in human serum cholesteryl esters by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 960 , 222-9, (2014) We described a rapid and precise method for simultaneous quantification of eleven fatty acids in human serum cholesteryl esters (CEFAs) by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)... |
|
|
Oxidized cholesteryl linoleates stimulate endothelial cells to bind monocytes via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway.
Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22(4) , 581-6, (2002) Oxidation products of cholesteryl esters have been shown to be present in oxidized low density lipoprotein and in atherosclerotic lesions. Monocyte adhesion to the endothelium is an initiating crucial... |
| Cholesterol Linoleate |
| (8ξ,9ξ,14ξ)-Cholest-5-en-3-yl (9Z,12Z)-9,12-octadecadienoate |
| Cholesteryl linoleate |
| EINECS 210-065-9 |
| 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid, (8ξ,9ξ,14ξ)-cholest-5-en-3-yl ester, (9Z,12Z)- |
| MFCD00003644 |