Isoastilbin
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 20:22:07
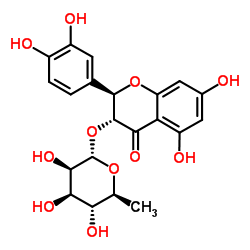
Isoastilbin structure
|
Common Name | Isoastilbin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54081-48-0 | Molecular Weight | 450.393 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 801.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O11 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 282.9±27.8 °C | |
Use of IsoastilbinIsoastilbin is a dihydroflavonol glycoside compound in Rhizoma Smilacis glabrae and Astragalus membranaceus. Isoastilbin inhibits glucosyltransferase (GTase) with an IC50 value of 54.3 μg/mL, and also inhibits tyrosinase activity. Isoastilbin shows neuroprotective, antioxidation, antimicrobial and anti-apoptotic properties and has the potential for Alzheimer’s disease research[1][21][3]. |
| Name | (2R,3S)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2 H-chromen-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranoside |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Isoastilbin is a dihydroflavonol glycoside compound in Rhizoma Smilacis glabrae and Astragalus membranaceus. Isoastilbin inhibits glucosyltransferase (GTase) with an IC50 value of 54.3 μg/mL, and also inhibits tyrosinase activity. Isoastilbin shows neuroprotective, antioxidation, antimicrobial and anti-apoptotic properties and has the potential for Alzheimer’s disease research[1][21][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 54.3 μg/mL (Glucosyltransferase (GTase)[2] |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 801.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H22O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 450.393 |
| Flash Point | 282.9±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 450.116211 |
| PSA | 186.37000 |
| LogP | 2.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.748 |
| InChIKey | ZROGCCBNZBKLEL-OOHAXVOVSA-N |
| SMILES | CC1OC(OC2C(=O)c3c(O)cc(O)cc3OC2c2ccc(O)c(O)c2)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3-[(6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-, (2R,3R)- |
| Astilbin Dihydroquercetin 3-rhamnoside Taxifolin 3-rhamnoside |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3-((6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-, (2R,3R)- |
| Taxifolin 3-rhamnoside |
| Neoisoastilbin |
| Astilbin |
| (2R-trans)-3-((6-Deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
| 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one, 3-((6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-, (2R-trans)- |
| Taxifolin 3-O-rhamnoside |
| Astilbin from Engelhardtia roxburghiana |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one |
| (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranoside |
| Isoastilbin |

