Quisqualic acid
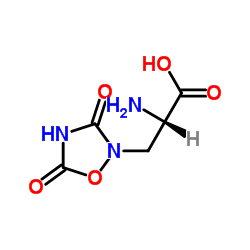
Quisqualic acid structure
|
Common Name | Quisqualic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52809-07-1 | Molecular Weight | 189.126 | |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 405.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H7N3O5 | Melting Point | 185-187ºC dec. | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 199.3±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Quisqualic acidQuisqualic acid (L-Quisqualic acid), a natural analog of glutamate, is a potent and pan two subsets (iGluR and mGluR) of excitatory amino acid (EAA) agonist with an EC50 of 45 nM and a Ki of 10 nM for mGluR1R. Quisqualic acid is isolated from the fruits of Quisqualis chinensis[1][2]. |
| Name | (+)-Quisqualic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Quisqualic acid (L-Quisqualic acid), a natural analog of glutamate, is a potent and pan two subsets (iGluR and mGluR) of excitatory amino acid (EAA) agonist with an EC50 of 45 nM and a Ki of 10 nM for mGluR1R. Quisqualic acid is isolated from the fruits of Quisqualis chinensis[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mGluR1R:45 nM (EC50) mGluR1R:10 nM (Ki) mGluR2R:108 μM (IC50) mGluR2R:113 μM (Ki) mGluR4R:593 μM (IC50) mGluR4R:112 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Quisqualic acid is an agonist of AMPA and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Quisqualic acid activates mGluR2R (EC50=108 μM; Ki=113 μM) and mGluR4R (EC50=593 μM; Ki=112 μM)[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 405.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 185-187ºC dec. |
| Molecular Formula | C5H7N3O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 189.126 |
| Flash Point | 199.3±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 189.038574 |
| PSA | 131.32000 |
| LogP | -1.85 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.726 |
|
~10% 
Quisqualic acid CAS#:52809-07-1 |
| Literature: Murakoshi, Isamu; Ikegami, Fumio; Yoneda, Yoshihiro; Ihara, Harumi; Sakata, Kumiko; Koide, Chiharu Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1986 , vol. 34, # 4 p. 1473 - 1478 |
|
~% 
Quisqualic acid CAS#:52809-07-1 |
| Literature: Ikegami, Fumio; Takayama, Kyoko; Tajima, Chiho; Murakoshi, Isamu Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1988 , vol. 27, # 7 p. 2011 - 2016 |
|
~% 
Quisqualic acid CAS#:52809-07-1 |
| Literature: Baldwin, Jack E.; Adlington, Robert M.; Birch, David J. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications, 1985 , # 5 p. 256 - 257 |
|
~% 
Quisqualic acid CAS#:52809-07-1 |
| Literature: Murakoshi, Isamu; Ikegami, Fumio; Koide, Chiharu Heterocycles, 1984 , vol. 21, # 2 p. 705 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain canc... |
|
|
Long-term administration of the antidepressant vilazodone modulates rat brain monoaminergic systems.
Neuropharmacology 99 , 696-704, (2015) Vilazodone has high affinity for the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1A (h5-HT1A) receptor and for the serotonin transporter (5-HTT). A previous in vivo microdialysis experiment showed that a single administ... |
|
|
Conformationally-restricted amino acid analogues bearing a distal sulfonic acid show selective inhibition of system [formula omitted]over the vesicular glutamate transporter
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20 , 2680-3, (2010) A panel of amino acid analogs and conformationally-restricted amino acids bearing a sulfonic acid were synthesized and tested for their ability to preferentially inhibit the obligate cysteine-glutamat... |
| L-Alanine, 3-(3-hydroxy-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-2(5H)-yl)- |
| L-Quisqualic acid |
| L-Alanine, 3-(3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidin-2-yl)- |
| 1,2,4-Oxadiazolidine-2-propanoic acid, α-amino-3,5-dioxo-, (S)- |
| MFCD00069337 |
| 3-(3,5-Dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidin-2-yl)-L-alanine |
| b-(3,5-Dioxo-1,2,4-oxodiazolidin-2-yl)-L-alanine |
| L-(+)-a-Amino-3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidine-2-propanoic Acid |
| (L)-(+)-a-Amino-3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidine-2-propanoic acid |
| Quisqualic acid |
| 3-(3-Hydroxy-5-oxo-1,2,4-oxadiazol-2(5H)-yl)-L-alanine |
| β-(3,5-Dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidin-2-yl)-L-alanine |
| L-Quisqualic acid,(L)-(+)-α-Amino-3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidine-2-propanoicacid |
| (S)-a-Amino-3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-oxadiazolidine-2-propanoic Acid |

 CAS#:1483-07-4
CAS#:1483-07-4