L-thyroxine
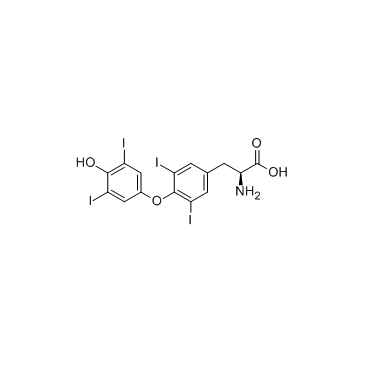
L-thyroxine structure
|
Common Name | L-thyroxine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 51-48-9 | Molecular Weight | 776.870 | |
| Density | 2.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 576.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H11I4NO4 | Melting Point | 235 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 302.3±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of L-thyroxineL-Thyroxine (Levothyroxine; T4) is a synthetic hormone in the treatment of hypothyroidism. DIO enzymes convert biologically active thyroid hormone (Triiodothyronine,T3) from L-Thyroxine (T4). |
| Name | L-thyroxine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Thyroxine (Levothyroxine; T4) is a synthetic hormone in the treatment of hypothyroidism. DIO enzymes convert biologically active thyroid hormone (Triiodothyronine,T3) from L-Thyroxine (T4). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | Deiodinases (DIOs), which catalyse the conversion of thyroxine (pro-hormone) to the active thyroid hormone, are associated with thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. DIO1 and DIO2 catalyze activation of thyroid hormone secretion in contrast to DIO3 playing role inactivation of the secretion. Activities of DIO1 and DIO2 play pivotal role in the negative feedback regulation of pituitary TSH secretion[1]. L-Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) hormones are known to modulate the expression of ionic channels, pumps and regulatory contractile proteins. Moreover, thyroid hormones have been shown to influence calcium homeostasis and flux responsible for excitation and contractility, with L-Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine modulating its pharmacological control and secretion. In rats fed 12 weeks with the iodine-free diet, a significant decrease in the levels of both Triiodothyronine and L-Thyroxine is observed when compared to the control group fed with standard diet (p<0.001). In the group treated with low doses of L-Thyroxine, an increase in L-Thyroxine levels is observed (p=0.02) while Triiodothyronine levels remain virtually similar to the control group (p=0.19). Rats treated with high doses of L-Thyroxine display a significant increase in both Triiodothyronine and L-Thyroxine circulating concentrations compared to the non-treated hypothyroid group (p<0.001 and p=0.004, respectively) and a significant increase in L-Thyroxine levels when compared to the control values (p=0.03)[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] Sprague-Dawley female rats (N=22) are used. Non-pregnant rats are divided into four groups: 1) control, 2) hypothyroidism, 3) hypothyroidism treated with low doses of L-Thyroxine (20 μg/kg/day) and 4) with high doses of L-Thyroxine (100 μg/kg/day). Control rats (group 1) are fed with standard diet, while the intervention rats are fed with iodine-free diet for 12 weeks to induce hypothyroidism (groups 2-4) which is continued for four more weeks to allow screening of hypothyroid status and L-Thyroxine-treatment. Food and water (iodine-free diet) are available ad libitum. The hypothyroid group treated with low (group 3) or high doses of L-Thyroxine (group 4) are injected intraperitoneally every 24 h with respectively 20 μg/kg/day and 100 μg/kg/day. Blood samples are collected for thyroid function screening at week 12 and 16 following the initiation of either the control or iodine-free diet. Hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia (isoflurane 2%) at the end of the treatment and the two uterine horns are placed in physiological Krebs' solution until isometric tension measurements within no more than 1 h. |
| References |
| Density | 2.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 576.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 235 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C15H11I4NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 776.870 |
| Flash Point | 302.3±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 776.686646 |
| PSA | 92.78000 |
| LogP | 5.93 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.795 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
Synonym:None Known Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Risk Phrases: 20/21/22 Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed.The toxicological properties of this material have not been fully investigated.Light sensitive. Potential Health Effects Eye: May cause eye irritation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. The toxicological properties of this substance have not been fully investigated. Chronic: No information found. Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid. Skin: Get medical aid if irritation develops or persists. Wash clothing before reuse. Flush skin with plenty of soap and water. Ingestion: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid. Do NOT induce vomiting. If conscious and alert, rinse mouth and drink 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Inhalation: Remove from exposure and move to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical aid. Notes to Physician: Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information: As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. During a fire, irritating and highly toxic gases may be generated by thermal decomposition or combustion. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution. Extinguishing Media: In case of fire, use water, dry chemical, chemical foam, or alcohol-resistant foam. Use agent most appropriate to extinguish fire. Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8. Spills/Leaks: Vacuum or sweep up material and place into a suitable disposal container. Clean up spills immediately, observing precautions in the Protective Equipment section. Avoid generating dusty conditions. Provide ventilation. Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling: Wash thoroughly after handling. Remove contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. Use with adequate ventilation. Minimize dust generation and accumulation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Keep container tightly closed. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Store protected from light. Storage: Keep container closed when not in use. Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances. Hormones and antibiotics room. Store protected from light. Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls: Good general ventilation should be sufficient to control airborne levels. Facilities storing or utilizing this material should be equipped with an eyewash facility and a safety shower. Exposure Limits CAS# 51-48-9: Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166. Skin: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Clothing: Wear appropriate protective clothing to minimize contact with skin. Respirators: Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Use a NIOSH/MSHA or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator if exposure limits are exceeded or if irritation or other symptoms are experienced. Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Solid Color: cream Odor: none reported pH: Not available. Vapor Pressure: Not available. Viscosity: Not available. Boiling Point: Not available. Freezing/Melting Point: Decomposes Autoignition Temperature: Not applicable. Flash Point: Not applicable. Explosion Limits, lower: Not available. Explosion Limits, upper: Not available. Decomposition Temperature: Not available. Solubility in water: Insoluble in water Specific Gravity/Density: Not available. Molecular Formula: C15H11I4NO4 Molecular Weight: 776.6993 Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability: Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. Conditions to Avoid: Incompatible materials, light, dust generation, excess heat, strong oxidants. Incompatibilities with Other Materials: Oxidizing agents, strong bases. Hazardous Decomposition Products: Nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, irritating and toxic fumes and gases, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen iodide. Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported. Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#: CAS# 51-48-9: YP2833500 LD50/LC50: Not available. Carcinogenicity: L-Thyroxine - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, or NTP. Other: See actual entry in RTECS for complete information. Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations. Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA Not regulated as a hazardous material. IMO Not regulated as a hazardous material. RID/ADR Not regulated as a hazardous material. Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives Hazard Symbols: XN Risk Phrases: R 20/21/22 Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. Safety Phrases: S 24/25 Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S 28A After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water. S 37 Wear suitable gloves. S 45 In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible). WGK (Water Danger/Protection) CAS# 51-48-9: 1 Canada CAS# 51-48-9 is listed on Canada's DSL List. CAS# 51-48-9 is not listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List. US FEDERAL TSCA CAS# 51-48-9 is listed on the TSCA inventory. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310 + P330-P302 + P352 + P312-P370 + P378 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | 2811.0 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YP2833500 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 6 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Inducible, tightly regulated and growth condition-independent transcription factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(17) , e130, (2014) The precise control of gene expression is essential in basic biological research as well as in biotechnological applications. Most regulated systems available in yeast enable only the overexpression o... |
|
|
Replisome-mediated translesion synthesis and leading strand template lesion skipping are competing bypass mechanisms.
J. Biol. Chem. 289(47) , 32811-23, (2014) A number of different enzymatic pathways have evolved to ensure that DNA replication can proceed past template base damage. These pathways include lesion skipping by the replisome, replication fork re... |
|
|
Levothyroxine replacement in hypothyroid humans reduces myocardial lipid load and improves cardiac function.
J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99(11) , E2341-6, (2014) Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder frequently accompanied by alterations in lipid metabolism, such as hypercholesterolemia and high circulating triglycerides, both risk factors for nonische... |
| Thyroxine (VAN) |
| b-((3,5-Diiodo-4-hydroxyphenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl)alanine |
| Thyroxine, L- (8CI) |
| EINECS 200-101-1 |
| (-)-3-[4-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]alanine |
| 3,3’,5,5‘’-Tetraiodo-L-thyronine |
| O-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine |
| 3-[4-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]-L-alanine |
| Thyroxine |
| L-3,5,3',5'-Tetraiodothyronine |
| thyroxine-binding globulin |
| (-)-Thyroxine |
| Thryroxine, l- |
| thyroxin |
| T4 |
| L-Thyroxine |
| Tetraiodothyronine |
| THX |
| L-Tyrosine, O-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenyl)-3,5-diiodo- |
| transthyretin |
| L-Thyroxin |
| Thyroxine, L- |
| Thyrax |
| l-t4 |
| Levothyroxine |
| 3,5,3',5'-Tetraiodothyronine |
| O-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-diidophenyl)-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine |
| 4-14-00-02373 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| thyroxinal |
| L-thyroxine zwitterion |
| (2S)-2-Amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3,5-diiodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid |
| Henning |
| MFCD00002596 |
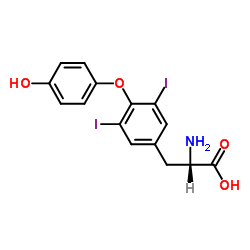 CAS#:1041-01-6
CAS#:1041-01-6 CAS#:300-30-1
CAS#:300-30-1 CAS#:1027-28-7
CAS#:1027-28-7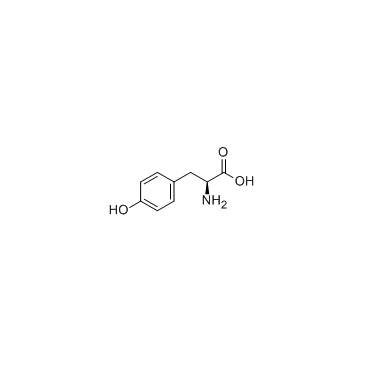 CAS#:60-18-4
CAS#:60-18-4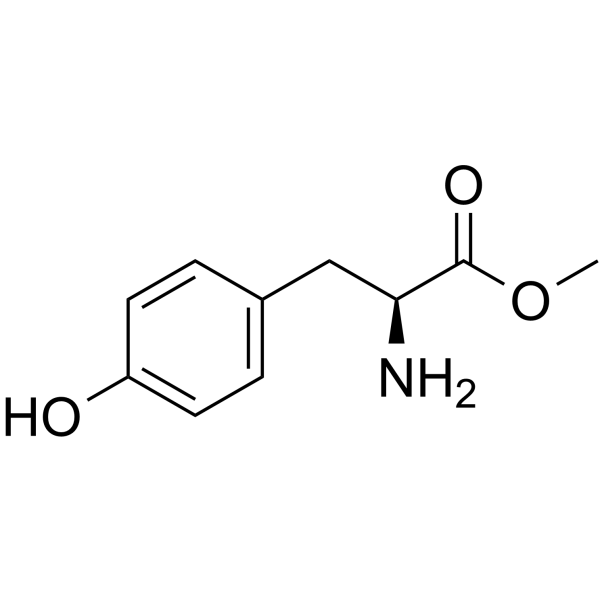 CAS#:1080-06-4
CAS#:1080-06-4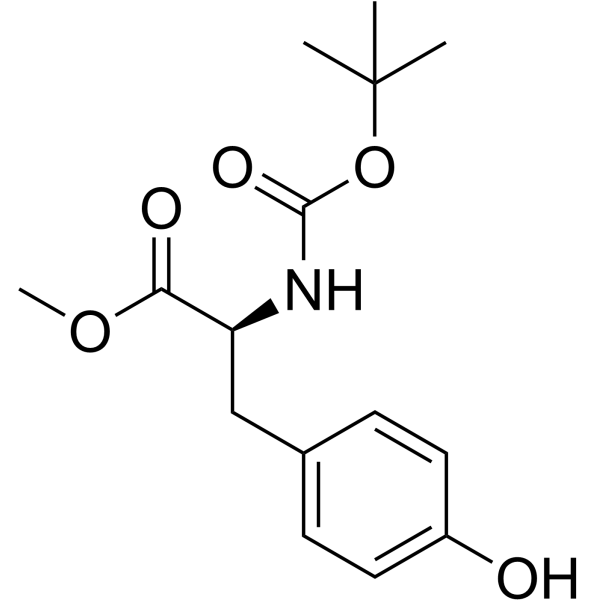 CAS#:4326-36-7
CAS#:4326-36-7 CAS#:128781-80-6
CAS#:128781-80-6 CAS#:26041-51-0
CAS#:26041-51-0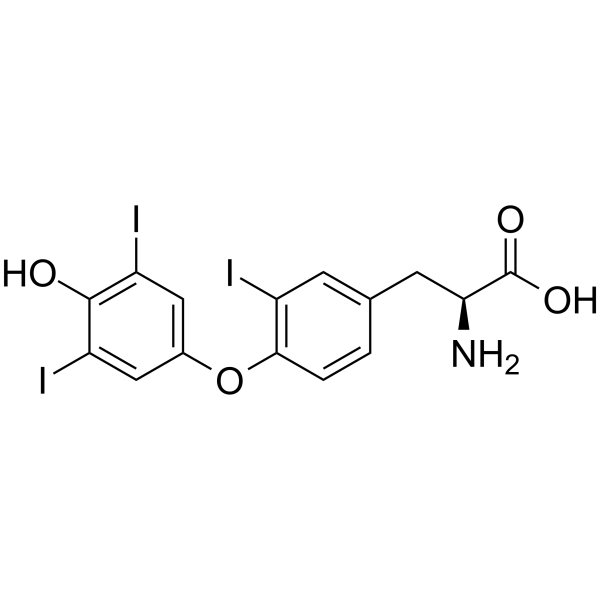 CAS#:5817-39-0
CAS#:5817-39-0![Naphtho[1,8-cd]-1,2-thiaselenole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/005/64869-35-8.png) CAS#:64869-35-8
CAS#:64869-35-8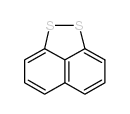 CAS#:209-22-3
CAS#:209-22-3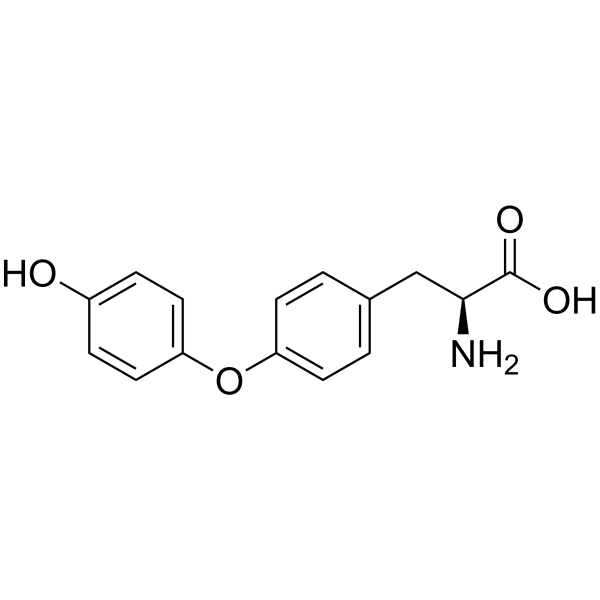 CAS#:1596-67-4
CAS#:1596-67-4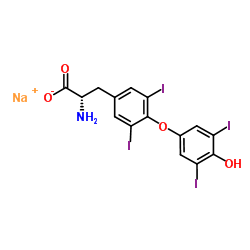 CAS#:55-03-8
CAS#:55-03-8
