D-3-Deoxyglucosone
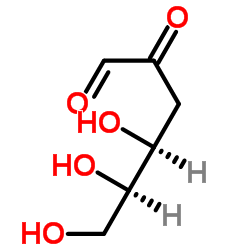
D-3-Deoxyglucosone structure
|
Common Name | D-3-Deoxyglucosone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4084-27-9 | Molecular Weight | 162.141 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 400.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O5 | Melting Point | 73-75ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 209.9±25.2 °C | |
Use of D-3-Deoxyglucosone3-Deoxyglucosone (3-Deoxy-D-glucosone) is a reactive intermediate of the Maillard reaction and the polyol pathway. 3-Deoxyglucosone rapidly reacts with protein amino groups to form advanced glycation end products (AGEs), such as imidazolone, it is the most specific AGE for 3-DG. 3-Deoxyglucosone synergizes with low glucose to potentiate GLP-1 secretion and is considered as a biomarker for diabetes[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 3-deoxyglucosone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 3-Deoxyglucosone (3-Deoxy-D-glucosone) is a reactive intermediate of the Maillard reaction and the polyol pathway. 3-Deoxyglucosone rapidly reacts with protein amino groups to form advanced glycation end products (AGEs), such as imidazolone, it is the most specific AGE for 3-DG. 3-Deoxyglucosone synergizes with low glucose to potentiate GLP-1 secretion and is considered as a biomarker for diabetes[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 3-Deoxyglucosone (80 ng/ml-1000 ng/ml; 1 hour) markedly increases GLP-1 secretion by 1.23-folds in 300 ng/ml or 1000 ng/ml 3DG-treated group. But at alower concentration (80 ng/ml) has no effects[1]. 3-Deoxyglucosone (300 ng/ml; 1 hour) dramatically increases intracellular Ca2+ levels by Fluo-3/AM determination (2.5 μM for 30 mins). But 3DG does not affect intracellular cAMP levels in a cAMP Elisa assay[1]. 3-Deoxyglucosone (300 ng/ml; 1 hour) significantly increases the protein expression levels of TAS1R2, TAS1R3, and TRPM5 under both glucose-free and highconditions[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: STC-1 cells Concentration: 300 ng/ml Incubation Time: 1 hour Result: Upregulated TAS1R2, TAS1R3, and TRPM5 expression. |
| In Vivo | 3-Deoxyglucosone (intragastric administration; 20 mg/kg; single dose) impairs glucose tolerance with increased AUC, but the plasma glucagon levels are not significantly different. It developes impaired glucose regulation (IGR) with obviously pancreatic islet cell dysfunction in kunming mice and SD-rats[2]. 3-deoxyglucosone (gastric gavage; 5-50 mg/kg; once daily; 2 weeks) is significantly increased in the upper small intestine (1.4-fold), lower small intestine (1.4-fold), ileum (1.4-fold) and colon (two fold) compared with the basal levels in the corresponding control group. In addition, the protein expressions of TAS1R2, TAS1R3 and TRPM5 in both duodenum and colon are significantly decreased[3]. Animal Model: SD rats[3] Dosage: 5, 20 and 50 mg/kg Administration: oral administration; once daily; 2 weeks Result: Was capable of accumulating in intestinal tissue and thereby decreased secretion of GLP-1 and insulin. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 400.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 73-75ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 162.141 |
| Flash Point | 209.9±25.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 162.052826 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | -2.38 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.512 |
| InChIKey | ZGCHLOWZNKRZSN-NTSWFWBYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=CC(=O)CC(O)C(O)CO |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
3-Deoxyglucosone: a potential glycating agent accountable for structural alteration in H3 histone protein through generation of different AGEs.
PLoS ONE 10(2) , e0116804, (2015) Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) are heterogeneous group of compounds, known to be implicated in diabetic complications. One of the consequences of the Maillard reaction is attributed to the pro... |
|
|
Studies on the Formation of Maillard and Caramelization Products from Glucosamine Incubated at 37 °C.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 6249-61, (2015) This experiment compared the in vitro degradation of glucosamine (GlcN), N-acetylglucosamine, and glucose in the presence of NH3 incubated at 37 °C in phosphate buffer from 0.5 to 12 days. The reactio... |
|
|
GC-MS Method for the Quantitation of Carbohydrate Intermediates in Glycation Systems.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5911-9, (2015) Glycation is a ubiquitous nonenzymatic reaction of carbonyl compounds with amino groups of peptides and proteins, resulting in the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) and thereby affec... |
| 3-Deoxy-D-erythro-hexos-2-ulose |
| 3-Deoxyglucosone |
| 3-Deoxy-D-erythro-hexosulose |
| (4S,5R)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-oxohexanal |
| D-erythro-Hexos-2-ulose, 3-deoxy- |