Maltohexaose
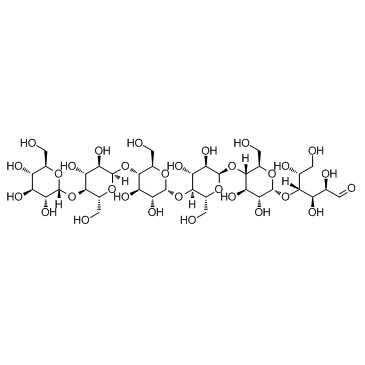
Maltohexaose structure
|
Common Name | Maltohexaose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34620-77-4 | Molecular Weight | 990.85900 | |
| Density | 1.87g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1307.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H62O31 | Melting Point | 204-206°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 744.7ºC | |
Use of MaltohexaoseMaltohexaose is a natural saccharide, and can be produced from amylose, amylopectin and whole starch. |
| Name | maltohexaose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Maltohexaose is a natural saccharide, and can be produced from amylose, amylopectin and whole starch. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.87g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1307.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 204-206°C |
| Molecular Formula | C36H62O31 |
| Molecular Weight | 990.85900 |
| Flash Point | 744.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 990.32800 |
| PSA | 506.13000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.4365 |
| InChIKey | OCIBBXPLUVYKCH-LIGGPISVSA-N |
| SMILES | OCC1OC(OC2C(CO)OC(OC3C(CO)OC(OC4C(CO)OC(OC5C(CO)OC(OC6C(CO)OC(O)C(O)C6O)C(O)C5O)C(O)C4O)C(O)C3O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Microbiota and metabolites of aged bottled gueuze beers converge to the same composition.
Food Microbiol. 47 , 1-11, (2015) Gueuze beers are prepared by mixing young and old lambic beers and are bottle-refermented spontaneously for aging. The present study analyzed the microbiota and metabolites present in gueuze beers tha... |
|
|
Octanoylation of early intermediates of mycobacterial methylglucose lipopolysaccharides.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13610, (2015) Mycobacteria synthesize unique intracellular methylglucose lipopolysaccharides (MGLP) proposed to modulate fatty acid metabolism. In addition to the partial esterification of glucose or methylglucose ... |
|
|
Tandem mass spectrometry of isomeric aniline-labeled N-glycans separated on porous graphitic carbon: Revealing the attachment position of terminal sialic acids and structures of neutral glycans.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29 , 1268-78, (2015) Quantitative monitoring of changes in the N-glycome upon disease has gained significance in the context of biomarker discovery. Separation and quantification of isobaric glycan isomers can be attained... |
| Maltohexaose,tech. |
| malto-hexaose |
| MFCD00083650 |
| Glc6 |
| maltohexanose,dp6 |
| AMYLOHEXAOSE |
| MALTOHEXAOSE |
| Maltohexose |

