D-Mannose
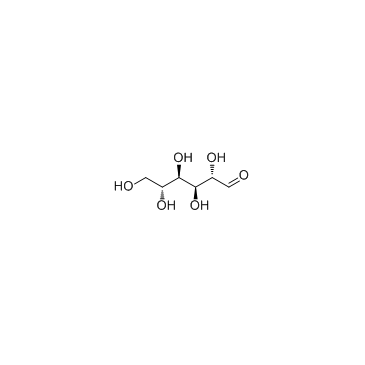
D-Mannose structure
|
Common Name | D-Mannose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 3458-28-4 | Molecular Weight | 180.156 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O6 | Melting Point | 133-140ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 286.7±26.6 °C | |
Use of D-MannoseD-Mannose is a carbohydrate, which plays an important role in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylationof specific proteins. |
| Name | α-D-mannose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Mannose is a carbohydrate, which plays an important role in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylationof specific proteins. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 527.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 133-140ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.156 |
| Flash Point | 286.7±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 180.063385 |
| PSA | 118.22000 |
| LogP | -3.17 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.573 |
| InChIKey | GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-KVTDHHQDSA-N |
| SMILES | O=CC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)CO |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2912491000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2912491000. other aldehyde-alcohols. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. polysaccharide ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipemia and vascular inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 164 , 229-38, (2015) Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC. (RG) has been widely used as traditional Chinese herbal medicine for treatment of diabetes and its complications. The polysaccharide fraction of RG has been proposed ... |
|
|
Preparation and structural characterization of poly-mannose synthesized by phosphoric acid catalyzation under microwave irradiation.
Carbohydr. Polym. 121 , 355-61, (2015) Poly-mannose with molecular weight of 2.457 kDa was synthesized using d-mannose as substrate and phosphoric acid as catalyst under the condition of microwave irradiation for the first time. The optimu... |
|
|
Type IV pilus glycosylation mediates resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to opsonic activities of the pulmonary surfactant protein A.
Infect. Immun. 83(4) , 1339-46, (2015) Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a major bacterial pathogen commonly associated with chronic lung infections in cystic fibrosis (CF). Previously, we have demonstrated that the type IV pilus (Tfp) of P. aerug... |
| D(+)-Maltose |
| alpha-D-mannose |
| (+)-Mannose |
| D-MAN |
| MFCD00064122 |
| (2S,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxyhexanal |
| Mannose |
| (2R,3R,4S,5S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal |
| D-(+)-Mannose,D-Mannopyranose |
| CARUBINOSE |
| Mannose, D- |
| D-(+)-Mannose |
| aldehydo-D-mannose |
| L-(-)-Mannose |
| aldehydo-D-manno-hexose |
| D-mannose |
| D-MANOSE |
| D(+)-Mannose |
| MANNOSE,D-(+) |
| D-Mannopyranose |
| d-mannos |
| D-(+)-Maose |
| SEMINOSE |
| EINECS 222-392-4 |
 CAS#:9004-34-6
CAS#:9004-34-6 CAS#:504-29-0
CAS#:504-29-0 CAS#:57-48-7
CAS#:57-48-7 CAS#:617-04-9
CAS#:617-04-9 CAS#:50-99-7
CAS#:50-99-7 CAS#:14199-83-8
CAS#:14199-83-8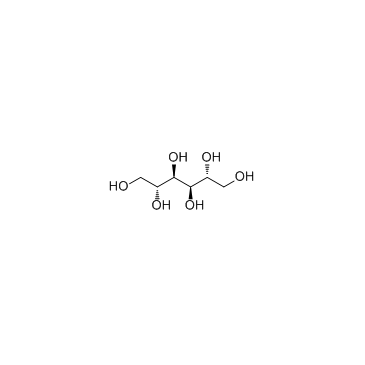 CAS#:69-65-8
CAS#:69-65-8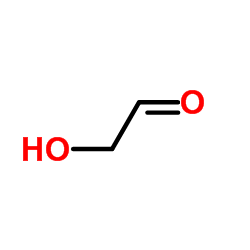 CAS#:141-46-8
CAS#:141-46-8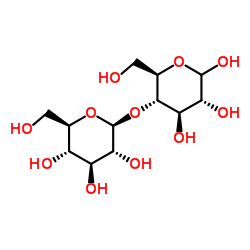 CAS#:133-99-3
CAS#:133-99-3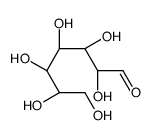 CAS#:10589-31-8
CAS#:10589-31-8 CAS#:492-93-3
CAS#:492-93-3 CAS#:642-99-9
CAS#:642-99-9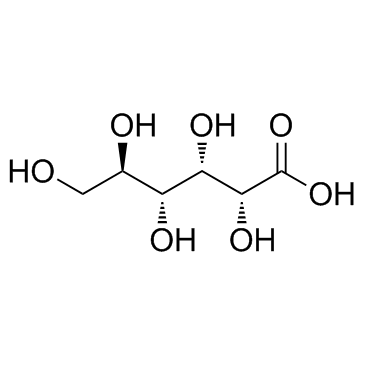 CAS#:526-95-4
CAS#:526-95-4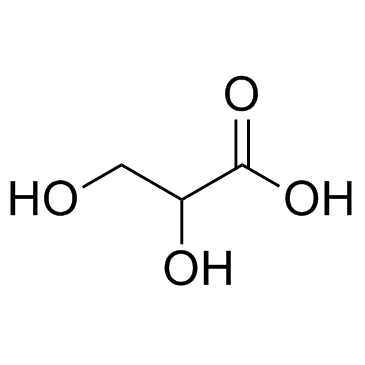 CAS#:473-81-4
CAS#:473-81-4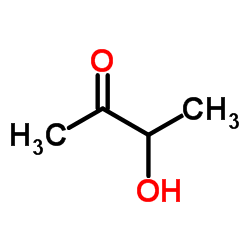 CAS#:513-86-0
CAS#:513-86-0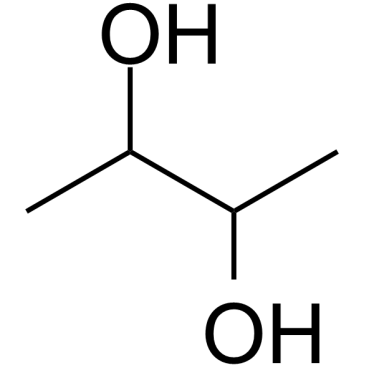 CAS#:513-85-9
CAS#:513-85-9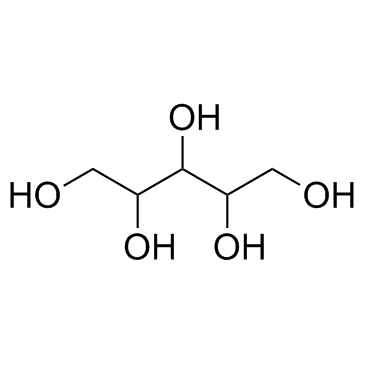 CAS#:488-82-4
CAS#:488-82-4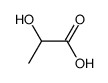 CAS#:849585-22-4
CAS#:849585-22-4
