(20S)-Protopanaxatriol
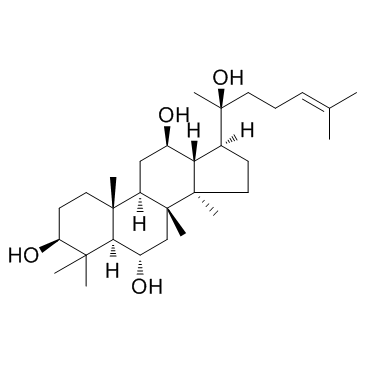
(20S)-Protopanaxatriol structure
|
Common Name | (20S)-Protopanaxatriol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34080-08-5 | Molecular Weight | 476.73 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 588.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H52O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 242.9±24.7 °C | |
Use of (20S)-Protopanaxatriol(20S)-Protopanaxatriol is a metabolite of ginsenoside, works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER), and is also a LXRα inhibitor. |
| Name | protopanaxatriol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (20S)-Protopanaxatriol is a metabolite of ginsenoside, works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER), and is also a LXRα inhibitor. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Glucocorticoid receptor, Oestrogen receptor[1], LXRα[2] |
| In Vitro | (20S)-Protopanaxatriol works through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and oestrogen receptor (ER) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (g-PPT) increases [Ca2+]i with an EC50 of 482 nM in HUVECs. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (1 µM) elevates NO production via ERβ[1]. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (PPT) inhibits the autonomous transactivation of Gal4-LXRα LBD, the T0901317-dependent transcription of SREBP-1c and its promoter. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol (10 μg/mL) blocks the recruitment of RNA polymerase II to the LXRE region of SREBP-1c. (20S)-Protopanaxatriol also inhibits T0901317-dependent transcription of LXRα target genes related to lipogenesis, and reduces T0901317-induced cellular triglyceride (TG) accumulation in primary hepatocytes, but does not alter transcription of ABCA1, also an LXRα target gene[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 588.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H52O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 476.73 |
| Flash Point | 242.9±24.7 °C |
| PSA | 80.92000 |
| LogP | 5.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.541 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Dual functions of ginsenosides in protecting human endothelial cells against influenza H9N2-induced inflammation and apoptosis.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 137 , 1542-1546, (2011) Panax ginseng is a precious traditional Chinese herbal medicine which has been utilized as herbal tonic for improving immunity. The active component, ginsenosides have been shown to possess various ph... |
|
|
Cytochrome P450 CYP716A53v2 catalyzes the formation of protopanaxatriol from protopanaxadiol during ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng.
Plant Cell Physiol. 53 , 1535-1545, (2012) Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) is one of the most popular medicinal herbs, and the root of this plant contains pharmacologically active components, called ginsenosides. Ginsenosides, a class of te... |
|
|
The in vitro structure-related anti-cancer activity of ginsenosides and their derivatives.
Molecules 16(12) , 10619-30, (2011) Panax ginseng has long been used in Asia as a herbal medicine for the prevention and treatment of various diseases, including cancer. The current study evaluated the cytotoxic potency against a variet... |
| PROTOPANAXTRIOL |
| 20(S)-APPT,g-PPT |
| Gonane-3,6,12-triol, 17-[(1S)-1-hydroxy-1,5-dimethyl-4-hexen-1-yl]-4,4,10,14-tetramethyl-, (3β,6α,12β,14β,17β)- |
| (3β,6α,12β,14β)-4,4,14-Trimethyl-18-norcholest-24-ene-3,6,12,20-tetrol |
| 20S-Protopanaxatriol |
| Protopanaxatriol, 20S- |
| (20S)-Protopanaxatriol |

